Viscose strength. Viscose is a synthetic material similar to natural fiber.
Origin
Viscose was first invented in 1884 by French scientist Guillier de Chardonnay. Natural viscose was a thick liquid, subsequently used in the production of fibers. The fibers began to be used to make leather and artificial fabrics. It found widespread use in the 20th century in the production of lingerie in the textile industry market.
Compound
Viscose, what kind of fabric? Of the various fibers of chemical origin, viscose is the most “natural”, because it is made from natural material: cellulose obtained from wood. Cellulose is produced from sawdust of pine, spruce, eucalyptus, bamboo stems and other species. By using modern technologies By changing the diameter and composition of the fiber, fabrics are obtained that cannot be distinguished from silk, woolen threads, linen or cotton. In appearance, pure viscose is opaque and shiny, for these qualities it is called “artificial silk”. To eliminate shine, viscose is diluted with special additives.
Positive properties

According to its characteristics, pure viscose is close to cotton; it is just as soft to the touch, hygroscopic and breathable. An excellent property of viscose is that it does not electrify. Viscose is very light, its threads are lighter than cotton. In addition, it lends itself perfectly to coloring; the dye can be diluted in the composition from which the viscose thread is made, and you can get any bright colors! Viscose, what kind of fabric? A distinctive property of viscose is its high hygroscopicity; it absorbs moisture twice as much as cotton! In addition, viscose has hypoallergenic properties, which is typical for natural materials. It washes well and dries quickly. In order to improve consumer properties, other fibers are added to viscose yarn and fabrics. For example, in order to increase strength, wear resistance - polyester, to preserve the properties of natural fabrics - cotton, linen, wool and silk, to acquire elasticity and the properties of a stretchable fabric - elastane or lycra. When moistened, pure viscose breaks down faster, but this property is easily corrected by weaving special durable fibers.
Flaws
Viscose, what kind of fabric? It also has its disadvantages.
- It wrinkles easily.
- Afraid of ultraviolet radiation.
- The fabric is fragile, especially when wet.
- Washing is possible at temperatures up to 60 degrees, but colored clothes are washed only in water at a temperature not exceeding 40 degrees.
 Application
Application
Over time, it became clear that viscose is excellent for finishing products and embroidery. Viscose, what kind of fabric is it, and how is it used now? It has found application in textiles and is also widely used in light industry. It makes excellent blouses, dresses, men's shirts, and trousers. It has found application in the production of children's clothing. Particularly popular are products made from viscose, which has a silky smooth finish; it is more durable and retains its attractive appearance longer. Viscose is used for sewing outerwear as lining material. Viscose is a material widely used in various options design in the field of nonwoven materials. In addition, due to its high ability to absorb moisture, viscose has found application in the manufacture of items such as tampons, wet wipes, cotton buds, cleaning wipes and sponges.
The viscose we are familiar with today was invented in 1884 by the French scientist Guillier de Chardonnay. Previous attempts by other researchers had failed. Viscose material gained great popularity 150 years later, in the twentieth century. Enterprises began to mass-produce clothes, linen from universal and diverse viscose. This is the only artificial fiber of natural origin. How can this be? Let's figure it out.
Description and characteristics of viscose fabric
What is viscose? Is it synthetic or natural fabric? The answer is clear - it’s not natural material. It is produced on the basis of natural cellulose (wood). Sawdust various breeds trees are turned into a thick liquid called cellulose xanthate. The wood is boiled in a solution of calcium hydrosulfite for a whole day under high pressure. Threads are formed from the resulting mass by pressing. Interestingly, if the same mass is pressed through thinner holes, then the well-known polyethylene film will be obtained.
Fabric structure
If we consider synthetic fibers used for textile production, then viscose is the most “natural” synthetic, because the sawdust (cellulose) used is of plant origin. Thanks to the use of modern technologies in production, fabrics are obtained that a non-specialist cannot distinguish from silk, linen or cotton. For the shine and smooth surface viscose is called "artificial silk". To give it a matte finish, it is diluted with special additives.
Properties and advantages
The properties of viscose fabric are very similar to natural ones, in particular to cotton. The material is soft to the touch, pleasant to the touch on the skin, looks ideal in products and has a number of other advantages. For example:
- Anti-allergenic. The material does not cause skin irritation even in people prone to dermatological problems.
- Breathability. Like cotton, viscose is a breathable material; the body does not get the “sauna effect”.
- Hygroscopicity. The material has high ability absorb moisture. This figure is twice as high as that of cotton.
- Antistatic. The fabric is not capable of accumulating static electricity and does not spark when rubbed.
- Thermoregulation. Viscose items keep you warm in winter, but not hot in summer.
- Permanent coloring. Diversity color range for dyeing, viscose is well accepted. The material does not fade, retains the brightness of colors for a long time.
- The fabric performed excellently in washing. Dries quickly.
Varieties of viscose
- Tencel (lyocell). This viscose is obtained from eucalyptus wood. According to the characteristics, the material is close to cotton, soft, pleasant, silky to the touch. Absorbs moisture well and is highly durable. Wrinkles easily. It is used for sewing bed linen, clothing, and home textiles.
- Modal. The quality is similar to cotton, but its hygroscopicity is one and a half times higher. Has high wear resistance. In combination with cotton fibers, modal is used for sewing bed textiles.
- Acetate. Cellulose waste – cellulose acetate – is used for production. The fabric is thin, with a slight shine, and looks like silk. Resistant to deformation, does not tolerate high temperatures, dissolves under the influence of acetone. Acetate is often used as a lining fabric.
- Cupra. The most expensive and high-quality type of viscose. Made from cotton cellulose. The material is close to silk in appearance and quality. It has high breathability, thermoregulation, and durability. Requires delicate care. Cupra fabric is used for sewing evening and festive dresses.
Answers to frequently asked questions
When purchasing a ready-made viscose product or fabric for individual tailoring, questions often arise regarding use: how the purchased item will behave during wear, during and after washing. According to their characteristics, all types of viscose material are similar to each other. Let's look at the most exciting moments regarding this fabric, based on reviews from people who use viscose products.
Viscose - stretches or not?
Unfortunately, viscose fabric in pure form will stretch. Due to this deficiency, clothing may lose shape and become deformed. To prevent this from happening and to prevent the buyer from being disappointed, when producing fabric, elastane or lycra is sometimes added to viscose, depending on the intended tailoring of the products. The elastane content in the fabric increases the wear resistance of the item and is not subject to excessive stretching, which is typical for stretch.
How to care for fabric
- Wash only on delicate cycle. Both manual and machine are allowed.
- Use soft detergents, better gel-like, without phosphates.
- Wash in water at a temperature of no more than 40 degrees.
- Due to the fact that viscose loses its strength properties when wet, twisting and hard pressing are not recommended.
- Dry away from heating devices, preferably horizontally.
- Iron from the wrong side on the “silk” setting, do not use steaming.
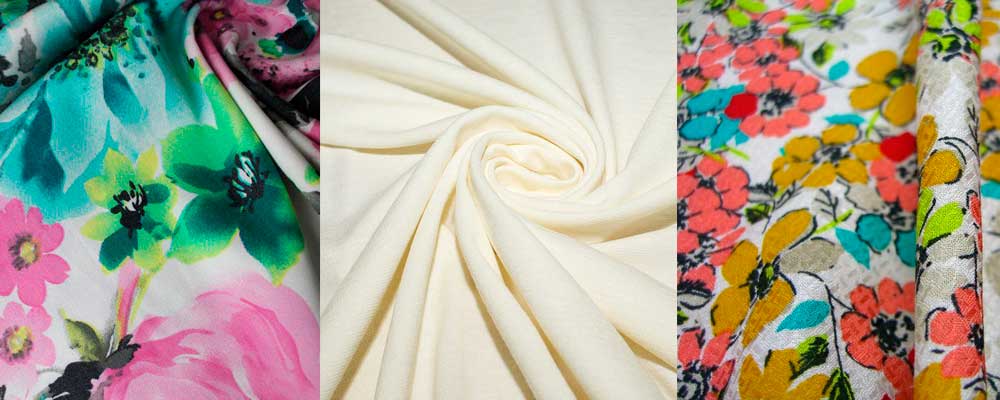
Photo: what viscose fabric looks like
To buy quality fabric, you need to know what it looks like. The selection of photos below will help you understand the differences. different types viscose according to external signs. Products based on this universal fabric look high-quality, elegant, and beautiful. With this knowledge, you can easily distinguish viscose from other fabrics on your own.
Video: what is viscose and what does it consist of?
Sometimes, to understand a certain issue, it’s easier to watch a video. If you prefer to receive information in this format, learn about the details of the production of viscose material by watching the video below. Having studied the entire process of creating things from this fabric, you will never confuse it with others. See how viscose is produced - a modern material that meets the high requirements of hypoallergenicity, hygroscopicity, breathability, and is beautiful in appearance.
A fabric comparable in strength and texture to silk - viscose - was introduced to the world by European textile workers more than two centuries ago. WITH early XIX centuries, English, German and Italian textile factories were computerized, and industrialists learned to mix threads, creating textures unique beauty and quality. Things made from natural viscose fibers - universal textiles, airy staple - are sewn fashion houses and clothing factories in the CIS countries, America, and Europe. Tablecloths, bed linen, dresses, trousers - and this is not all types of things made of hypoallergenic and practical material.
What is viscose
Viscose fiber consists of natural cellulose. The properties of the threads - strength, thickness, wear resistance - depend on the method of processing the raw materials. Cuts of fabric from threads in different ways the treatments are strikingly different in texture and can resemble silk, cotton, or wool.
History of appearance
Xanthogenation - the formation of fibers from a cellulose solution - was invented by the Englishmen Charles Cross, Edward Bevan and Clayton Beadle in 1891. In 1902, the Frenchman J. Brandenberger patented the technology. A chemist by training, he dedicated most life working with viscose fiber - I looked for ways to reduce the cost of the material, discovered a method of continuously squeezing cellophane film through a filler plate into an acid bath.
How and from what it is produced
In the 21st century, the production process of viscose fibers in industrial conditions includes four stages:
- Mixing a spinning solution from cardboard with the addition of dye;
- Automated forcing of the solution through the filler plate into the acid bath for thread formation;
- Treatment;
- Drying.
Cardboard sheets are prepared in the workshops of woodworking enterprises. Wood chips are dissolved in an alkaline solution and the resulting mass, previously bleached, is pressed into the sheet component of the future fabric.
Types and fashions of viscose fabric
- Staple is a common type of material with a base of viscose threads. The main disadvantage of staples is shrinkage. To sew a dress or skirt from it, you will need fabric 1.5-2 times larger than if you chose cotton or linen.
- Linen-viscose fabrics - linen yarn, viscose and synthetics in a mixture provide high hygroscopicity and delicate drapery folds. Bed and underwear, nightgowns and pajamas are often made from a mixture of linen and viscose.
- Jacquard viscose - the material belongs to decorative artificial fabrics. The jacquard pattern is burned on it with acid, which dissolves only natural viscose and preserves the synthetic frame.

Properties
- Air permeability - viscose does not interfere with normal air exchange, hence the popularity of the staple variety for sewing summer clothes.
- Softness - artificial silk is soft, therefore, like natural silk, classic and children's bedding sets are sewn from it.
- Practicality - things retain their color, do not rub or wrinkle after numerous washes.
- Attractive appearance- smooth texture and neat drapery of viscose decorate elegant dresses, bed sets and textured tablecloths.
Which is better: cotton or viscose
Viscose may be mistakenly classified as synthetics, preferring cotton to it. In fact, both materials are natural, the composition includes cellulose, and the properties are 90% the same. It is difficult to say unequivocally which is better - cotton or viscose, depending on the method of application and the required qualities.
Cotton is good when elasticity is not so important: for sewing shirts or sheets. Artificial silk wins in the world of women's and children's clothing, where in addition to hygroscopicity and softness, a variety of colors and retention of brightness after washing are important. Often materials are combined to create multi-layered clothing, linen, mattress covers, etc.
Features of use and care
Fabric requires careful care to maintain its properties and appearance. Manufacturers, in accordance with GOST restrictions on designations and markings, indicate on the label that the item requires careful washing, drying and ironing. Under no circumstances should it be bleached - aggressive components are dangerous for wood fibers. Twisting and drying on a line is also undesirable, as this can lead to shrinkage or deformation of the item.
A typical care regimen for viscose clothing and home textiles is hand washing, horizontal drying on a towel and ironing with a warm iron without steaming.
The quality and cost of viscose depends on the place and method of production. Asian combined fabrics with synthetic reinforcing fibers, elastin, cotton and linen are cheap and widespread, while English and French glazing beads are sometimes more expensive than silk. European fabrics upper class used by famous designers to sew fashion collections.
Until the beginning of the last century, only natural fabric was used for clothing, for which fibers of plant or animal origin were used. For several centuries, attempts were made to find a replacement for them, and some success in this area was achieved in late XIX century. The first patent for fiber obtained from processed cellulose was issued in 1884 to the Frenchman Guillier de Chardonnay, and the first rayon fabric was obtained in England in 1893. Since then, artificial fibers have been extremely widely used. Although the raw material for their production is still cellulose, the properties of the fabric obtained from such raw materials, as well as its appearance and purpose, can be very diverse.
Preparation and varieties
In order to understand what viscose is, what kind of fabric is produced on its basis and what its characteristics may be, you need to understand that it is a fairly large mass of artificial materials. Unlike natural fibers, directly obtained from animals or plants, or synthetic materials, which are obtained by synthesizing oil and gas products, the composition of viscose is cellulose, treated with one or another type of solvent, and formed into threads or film (cellophane) .
Its name, which comes from Latin word“sticky”, this material received due to the viscosity of the substance from which its fibers are formed. The most common method is to dissolve crushed wood or cotton floss with caustic soda, as a result of which you can obtain both thin shiny threads reminiscent of silk and fluffy fiber with a woolen texture. Regardless of the method of obtaining the cellulose solution, the production of viscose is carried out in the following sequence:
- cleaning, grinding and pre-processing of raw materials;
- dissolving and removing excess liquid;
- pressing viscose mass through dies and forming fibers;
- their subsequent processing (drying, pressing, bleaching, painting, etc.).
The resulting threads can be textile, technical or staple.
- They are made from thin and not particularly strong textile fibers. various fabrics and viscose knitwear, they are also used as an additive to other fibers when creating mixed fabrics.
- Larger and stronger technical threads are used for the manufacture of cord materials.
- A special category is staple fiber, which is short in length. Staple fabrics, artificial fur, and non-woven materials are made from it.
- In great demand in Lately I use viscose for felting, which is particularly soft and easy to work with.

Artificial fabrics can be classified according to the characteristics of their production, methods of fiber processing, and the composition of the raw materials. Among the many varieties of artificial materials, the following can be distinguished:
- acetate (triacetate) silk, which is shiny, wrinkles little and is quite dimensional stable;
- cellwolle is a staple fiber with a structure reminiscent of wool, used as a substitute;
- cupra is an elite fabric based on copper-ammonia fibers, the properties of which are close to natural silk;
- modal - improved viscose based on eucalyptus, pine or beech, refers to environmentally friendly materials;
- tencel (lyocell) - fabric made from eucalyptus cellulose, processed according to innovative technologies, characterized by durability and antiseptic properties;
- Siblon - improved viscose based on coniferous wood;
- polynose materials - viscose materials with a uniform fiber structure, characterized by increased strength and elasticity;
- bamboo is a material based on bamboo cellulose, which in its properties is most similar to natural cotton; cellulose mass for it is often obtained without the use of strong chemicals by mechanical crushing and natural fermentation (the so-called bamboo flax).

Properties of artificial materials
Viscose fabrics can resemble any natural material, from the finest silk to fur; moreover, they are very hygienic, pleasant to the touch, do not cause skin irritation, and are able to regulate temperature at the surface of the body, unlike most types of synthetics. The main advantages of all types of viscose are:
- softness and pleasant tactile sensations;
- high hygroscopicity;
- breathability;
- "warming" properties;
- color fastness;
- variety of textures;
- lack of electrification;
- low price (for most varieties);
- ease of disposal.
However, this material also has significant disadvantages. First of all, it is not very durable and not durable when wet, and quickly loses its appearance when exposed to ultraviolet radiation. All artificial materials They wrinkle heavily and are highly flammable. It should also be noted that positive properties often turn into disadvantages: for example, good hygroscopicity leads to undesirable absorption of moisture, and some varieties of such fabrics, such as bamboo, can become moldy in a humid atmosphere. Excessive softness leads to the fact that these products do not hold their shape well, and without special processing, folds and gathers cannot be created on them.
It is difficult to give a definite answer to the question of whether viscose shrinks. Fabrics that are produced using traditional technology can shrink a lot. Upgraded materials are produced with a special treatment that prevents shrinkage and makes the fabric dimensionally stable. It is also difficult to answer whether viscose stretches or not. Knitted, viscose knitwear is very elastic, and in order for woven fabrics to stretch, they need to add elastane. Thus, in order to avoid undesirable characteristics of clothing, you need to carefully study the composition of the fabric before buying. Most often, the content of viscose does not exceed 30%, in which case its undesirable properties practically do not appear.
Application and care
Most buyers are not aware that artificial materials are widely used as packaging, in the production of artificial leather and technical fabrics. It should be noted that both clothes made from pure viscose and viscose knitwear are now much less common than half a century ago. Basically, this material is used in mass Indian textiles, it is often used as a lining for inexpensive accessories. This does not apply to such modern materials like bamboo, modal, tencel, etc. They are often used for sewing a variety of clothes, linens, bedding sets. The absorbing properties of viscose fabric make it very popular in the production of towels, bath accessories, cleaning accessories.
Chemist and engineer Hilair de Chardonnay was the first to figure out how to turn wood into textile fibers. This is how viscose was born in the 19th century. The invention was so successful that after more than one hundred years this fabric is still popular. Depending on the production technology, it can look very different. Viscose is used to sew clothes and home textiles (about viscose bed linen), make cellophane and make boots. In the textile industry, viscose fibers are woven into fabrics resembling silk, wool, cotton or linen.

The industry produces several types of viscose fibers:
- technical;
- textile;
- staple.
The properties of such dissimilar, at first glance, textile and staple viscose fibers are largely similar. Viscose is an artificial fabric, but not synthetic. What is this material made of? In the production of the material, natural raw materials are used - wood pulp. This affected the properties of the material. Sometimes the fabric is called natural synthetics.
The physical and mechanical properties of viscose depend on the method of fiber spinning. The fabric can be shiny or matte, dense or light, textured or smooth. Pure viscose is similar to silk: it is translucent and shiny. They get rid of shine by introducing special matting substances.

Advantages of the material:
- The fabric is soft and pleasant to the touch, warm in winter and cool in summer
- The fabric drapes well.
- Viscose does not accumulate static electricity.
- The fibers are easily dyed in any bright colors. The dyeing technology involves the introduction of the dye directly into the fibers.
- Properly dyed fabric does not fade.
- Viscose is lighter than cotton.
- Compared to cotton, viscose absorbs moisture twice as much.
- Dry fabric has high strength.
- The fabric does not require special disposal.
- Does not cause allergies.
- Has high hygienic properties.
What viscose looks like can be seen in this photo:

The disadvantages include some difficulties in caring for the fabric, especially high wrinkling. Another unpleasant moment - viscose can shrink, roll and deform during washing. The descriptions also note the wear of the fabric under the influence of water, high temperature, ultraviolet radiation. Especially if these factors act simultaneously. Therefore, even at the stage of fiber production, chemical antioxidants and ultraviolet filters are introduced into them.
Kinds
Viscose is used to produce not only fabrics, but also non-woven materials used in light industry. Viscose fiber is produced colorless or dyed in the mass. The most popular types of viscose in light industry resemble natural fabrics.

Comparison with other fabrics

The plant fibers in viscose fabric made it look like cotton. What is better than them? Viscose also absorbs moisture well, is pleasant to the touch and breathable. These fabrics are sometimes confused. They are really very similar. However, viscose is a less durable fabric and wears out faster. While cotton is a very strong fabric even when wet, viscose becomes vulnerable in water. But considering the low price, this drawback can be considered insignificant.
In the sun, viscose may develop spots of a different, unusual color. This is how it can react to the action of ultraviolet radiation. Modern fabric manufacturers have learned to deal with these troubles. Viscose undergoes a special treatment that increases its strength. The use of staple fibers also has a positive effect on the quality of the fabric.

Viscose is a man-made fiber and is sometimes compared to polyester. But these are completely different fabrics. The natural raw material of viscose has equated the material, according to some indicators, to natural fabrics. If you have a choice between polyester and viscose, viscose will be the winner. It is hygroscopic and breathable, which cannot be said about polyester.
Prices

The cost of fabric depends on its composition, density, manufacturer, and variety. Viscose production is developing in the world. IN Soviet times Russia produced viscose in many factories. Then this direction stopped developing. Almost all the viscose on our shelves is imported. The main supplier of raw materials for the production of viscose is China. He is also the largest fabric manufacturer. This industry is actively developing in Uzbekistan.
However, fabrics from domestic manufacturers are also appearing on the market. They mainly produce lining fabrics from viscose. The price of 1 meter of such lining twill is 250 rubles. viscose lining from Italy is more expensive. Its price is about 700-900 rubles. per meter
A meter of fine viscose knitwear can be bought for 700–900 rubles. Dense material will cost more. Printed viscose made in China will cost 500–700 rubles. per meter with a width of 1.45 m. Crepe viscose from the same manufacturer is in the same range.
In the segment of more noble viscose fabrics, prices start from several thousand and end in tens of thousands per linear meter. The width of viscose is usually in the range of 1.40–1.50 m.