Types of clock mechanisms. Commodity dictionary
Auto-quartz movement
Combination of automatic and quartz movement. As a result of everyday hand movements, the generator charges the watch's mini-battery. The energy of a fully charged battery is enough for 50-100 days of uninterrupted operation of the watch.
Automatic mechanism
The most common type of mechanism used in mechanical watches today. In such a mechanism, the spring is wound by a rotor that wraps around the main axis of the watch. For a watch with an automatic movement to wind, the usual everyday movements of the hand are quite enough - no special movements are required. Automatic watches are heavier and thicker than simple quartz or mechanical watches due to the rotor that winds them.
Shock absorbers
Special devices necessary to protect mechanism parts from possible damage due to impulse loads. The most common shock absorption system today is Incabloc. The system of Abraham-Louis Breguet called “para-chute” is also widely known.
Anchor mechanism (anchor)
The anchor or anchor mechanism is the part of the watch mechanism that converts the energy of the mainspring into impulses - these are transmitted to the balance to maintain the required period hesitation. This is necessary for uniform and precise rotation of the gear mechanism. The anchor mechanism is a structure consisting of a fork, a double pendulum, a balance and an escape wheel.
Aperture
A small window (hole) in a watch dial. It gives the current indication of the day of the week, date, etc.
Astronomical clock
Clock displaying moon phases, sunrise and sunset times. Some models of such watches can also display the movement of planets and constellations of the solar system.
Baguette
This is a clock mechanism with an elongated rectangular shape.
Balance
The balance is a balance wheel and a spiral, which together form an oscillating system. This system balances the movement of the gear mechanism in the watch.
Bezel
A rim or ring around the dial. This ring can be rotary, rotating in both or one direction. The fixed ring (or bezel) often serves a decorative function. A tachometer or seconds scale can be applied to it, and the bezel can be encrusted with precious stones. If it is a rotating bezel, then it can serve to record or measure the time of a certain event. Most often, a rotating bezel is seen on diving watches.
Water resistance
The widely used ability of a watch case to protect the watch mechanism by preventing moisture from entering it. The value of water resistance, its degree is calculated in atmospheres or meters. In this case, immersion in water 10 meters deep is equal to an increase in pressure by 1 atmosphere. However, it is important to understand that the water resistance of a watch to 50 meters does not mean that you can dive to a depth of 50 meters with it. Even when a person swims on the surface of the water, any watch is subject to pressure equal to the static pressure of water at a level of 60-70 m depth.
Helium valve
The watch used for scuba diving has a built-in helium decompression valve. When carrying out long-term deep-sea work, a diving bell is used, which is filled with a mixture of oxygen and helium. Considering that helium molecules are lighter in weight than air molecules, helium can penetrate inside the watch and then squeeze out the watch crystal during decompression. To avoid this, it is necessary to open the helium valve during ascent (ascent) to the surface - it allows helium to pass through, but at the same time retains water.
Guilloche
A method of finishing a watch dial that uses an engraving machine to create designs that are a combination of curves and simple lines.
Yearly calendar
A calendar device built into the watch, containing indicators of the month, day of the week, and date. In this case, there is no need to adjust the date, except for February 29 in leap years.
Two-tone watch
A watch whose bracelet or case (or both) is made of a compound different materials. For example, it could be a watch made of stainless steel and gold or gold and silver.
Dynamograph
Indicator of the force produced by the drum spring.
Winding the watch
The procedure for winding a watch's mainspring. This operation can be performed automatically or manually. If twisting is done manually, the spring is wound using the crown provided in the watch. For automatic winding, it is necessary to use the rotation of the rotor, which converts rotational energy into the energy needed to twist the mainspring.
Crown
A special part of the watch case, necessary for winding the watch, as well as for correcting the date and time.
Zalium
A special, unique alloy that was developed by engineer and chemist Ronald Winston. The invention of this alloy is based on zirconium, which has greater corrosion resistance and strength than titanium. This alloy is considered rare because zirconium is much more difficult to find on Earth than titanium. In addition, zirconium, due to its exceptional hardness, is less easy to process. Zalium is harder and heavier than titanium, while it is anti-corrosion and hypoallergenic.
Power reserve mechanical watch
The length of time a watch can operate without winding the mainspring and maintaining its normal functioning. Typically range wristwatch, which are fully wound up, is approximately 40-46 hours.
Power reserve indicator
An indicator made in the form of an additional sector that shows the degree of winding of the mainspring in a mechanical watch. This indicator shows the time remaining until the clock stops. Time can be displayed in hours and days (absolute units) or in relative units.
Moon phase indicator
Rotating indicator with the image of the Moon, which at each moment of time shows the phase of the Moon in this moment. The dial has a graduation of 29 days.
Cabochon
Cutting method precious stones when they are processed into a hemispherical shape. Typically, cabochons are used to decorate watches: the crown of the watch is decorated, and the lugs that attach the strap to the watch case and the bracelet are inlaid with cabochons.
Calendar
The simplest calendar in a watch is a window in which you can see the current date. In a more complex version, the calendar window shows the month, day of the week and date. Of all the calendars, the most complex is the perpetual calendar, which also indicates the year. In a perpetual calendar, there is no need to adjust the date of the month even if it falls leap year. As a rule, such calendars are programmed for 100-250 years.
Caliber
This term refers to the type and size of the watch movement. Typically, the caliber number corresponds to the maximum overall size of the watch movement, which is measured in lines. The line is 2.255 mm. In some cases, the caliber is a regular set of symbols that designate a particular model.
Stones
This term refers to watch parts made from rubies, garnets or sapphires (both natural and artificial stones can be used) used to reduce friction between metal parts.
Quartz movement
This is a clockwork mechanism that is powered by a battery that lasts approximately 3 years. Watches with quartz movements are highly accurate. These watches do not need to be wound. In such watches, the time-setting element is a quartz resonator, which is a processed in a special way a plate made from an artificially obtained quartz crystal. This plate is compressed under voltage and generates electrical impulses.
Line
A standard measure of the size of a watch movement. The line is 2.255 mm.
Maltese cross
The Maltese cross is an element of the watch mechanism, which is necessary to limit the tension force of the main (winding) spring. This item got this interesting name because of its resemblance to the Maltese cross.
Marquetry
A set of thin wooden plates 1-3 mm thick. Wood (veneer) is used in their manufacture. different breeds. It can be myrtle, lemon, sandalwood, burl poplar, walnut, oak, ash, maple, pear or apple tree, etc. The veneer of these species is an excellent material. The plates are glued along the edges in the form of an ornament or design, and then glued to a flat wooden surface.
Marine chronometer
This is a particularly precise watch, which is placed in a special case. The case constantly holds the clock mechanism in a horizontal position. Such mechanical watches are used to determine latitude and longitude in the ocean. Thanks to a special case, the influence of gravity and temperature on the accuracy of the watch movement is completely eliminated.
Bridge
This is a shaped part of a watch mechanism, necessary for securing the supports of the gear axes in the watch. The bridge is named according to the gear it is attached to.
Cloisonne enamel
Special view enamel, in the production of which complex technology is used. The essence of this technology is this: deep recesses are made in the dial into which the wire is laid. The remaining gaps between the wires are filled with a layer of powder. After firing, the powder turns into hardened enamel. Subsequently, the resulting enamel is polished.
Platinum
The largest, main part of the watch mechanism frame. This part is used to secure gears and axles. The shape of this part determines the shape of the watch mechanism.
Gilding
Plating a bracelet and/or watch case made of steel with a thin layer of gold. The most common gold plates are 5 and 10 micrometers thick. Today, PVD coating is considered very popular. In this case, super-hard titanium nitride is applied to the material from which the watch case is made in a vacuum. A thin layer of gold is applied on top of this coating. This coating is highly resistant to scratches and wear, while gold plating wears off at a rate of approximately 1 micron/year. Another coating option is Ion Plating Gold(IPG) - is an ion sputtering of gold with an intermediate hypoallergenic layer. This is the most wear-resistant gold plating.
Shockproof device
A device consisting of movable supports in which thin parts of the balance axis are fixed. This movable support is made in such a way that during a lateral or axial impact, the balance axis moves sideways or upwards and its thickened parts rest against the limiters. This prevents the thin parts of the axle from bending and breaking. The very first protection of this type was invented in 1790. It was called para-chute. The most common shockproof device today is Incabloc.
Heart rate monitor
A scale on a dial with a chronograph, which allows you to determine a person’s pulse in a fairly short period of time according to the gradation of the scale.
Repeater
Mechanical watches that have an additional mechanism. This mechanism is designed to indicate time using signals (sounds) of different tones. Most often, such a clock, if you press a certain button, chimes the hours, minutes, quarter hours.
Rotor
A half-disc made of heavy metal freely rotating around the clock axis. This disk, with the help of a reversing device, converts the energy of its rotation into the energy needed to wind the spring in the watch.
Manual winding mechanism
Mechanical watches are supplied with the energy necessary for their operation by a spiral spring, which is located in a drum with a serrated edge. When the watch is wound, the spring is twisted, and then it slowly unwinds and drives the drum, which, in turn, by its rotation makes the entire clock mechanism work. The biggest disadvantage of a spring motor is the uneven speed of unwinding of the spring. As a result, the clock is inaccurate. Besides, in in this case The accuracy of the watch is also affected by such factors as the position of the watch, temperature, wear of parts, etc. Mechanical watches that are manually wound must be wound using the crown located on the case.
Second
A unit of time that denotes a time interval equal to 9,192,631,770 periods of radiation from a cesium-133 atom during the transition between two adjacent stable levels. A second is equal to 1/60 of a minute and 1/3600 of an hour.
Skeleton
A watch with a transparent dial, as well as a case back, through which you can see the operation of a complex clock mechanism. Often the mechanism parts in such watches are skillfully decorated with engraving, covered with various precious metals, and inlaid with precious stones.
Breguet spiral
This is a spiral in which the outer and inner ends are bent so that the period of oscillation of the spiral-balance system is not related to the amplitude of the oscillations. This invention is the achievement of Abraham-Louis Breguet, which is reflected in the name of the spiral.
Spiral or hair
A flat thin spiral spring, which is fixed with its outer end to the block, and with its inner end on the balance axis. Typically, the number of turns of this spiral is 11 or 13. Thanks to Huygens's invention of the spiral-balance oscillatory system, it became possible to create the first portable watch.
Split chronograph
This is a chronograph with a mid-finish function. In a split-seconds chronograph, the mechanism expands the functions of a conventional chronograph with the ability to measure 2 or more events that begin simultaneously, but have different durations. These chronograph models have two central seconds hands. A special button makes it possible to stop the second arrow as many times as necessary, and then start it again “from scratch”. The first arrow continues its movement.
Tonneau
Barrel-shaped watch case.
Trust index
This is an indicator of the amplitude of the balance wheel. If the spring is fully wound, then the amplitude of oscillation of the balancer in a conventional mechanical watch is slightly higher than the optimal value. When the winding of the spring comes to an end, the amplitude of the balancer oscillations, on the contrary, is slightly less. Therefore, to maintain maximum watch accuracy, it is not recommended to over-tighten the spring or allow it to completely discharge.
Tourbillon
A special mechanism that compensates for the influence of our planet’s gravity on the accuracy of the watch. This is an anchor mechanism that is placed inside mobile platform, in the center of which is balance. The mechanism makes a full revolution around its axis in a minute. The tourbillon is installed in luxury and expensive watches.
Ultra-thin watch
Watch models with a mechanism thickness of 1.5-3.0 mm, which allows you to reduce the thickness of the watch itself to a minimum.
Equation of time
This is an astronomical value that takes into account the difference (discrepancy) between the generally accepted time (as shown by the clock) and solar time. These indicators coincide only 4 times a year.
Oyster
A Rolex model that has become widely known. This is also a method of double sealing the watch mechanism, patented by this company, protecting it from various external influences which may damage the mechanism.
Flyback chronograph
A chronograph with a fly-back function that allows you to start counting the seconds again with just one press of the reset button.
Chronograph
This is a watch that has two independent measuring systems. One system shows the current time, and the second system measures short periods of time (stopwatch). The available counter records the elapsed hours, minutes and seconds. This counter can be turned on and off at will. As a rule, in such watches the second hand is also the second hand of the stopwatch.
Chronographs are different. For example, a cumulative chronograph has two pushers. One button is needed to start and stop the stopwatch. The number of starts is not limited, but when the last stop is made, the chronograph shows the total duration of all these periods of time. The other button is necessary to reset the readings and only works when the stopwatch is stopped.
Also in the chronograph family there are models with the fly-back function, “monopushers”, which implement all counter control using one button, and split-seconds chronographs.
Chronometer
This is a particularly accurate watch. These watches undergo a number of accuracy tests and have an appropriate certificate. Mechanical chronometers have a running error of several seconds per day if they are used in a normal temperature range. At the same time, only those watches whose mechanism has received a COSC certificate can bear the proud title of “chronometer”.
COSC
Controle Officiel Suisse des Chronometres - translated as the Official Swiss Chronometer Testing Institute.
PVD
PVD stands for Physical Vapor Deposition. Today, the use of PVD coatings has become very popular as it is a very durable coating. Super-hard titanium nitride is applied to the material from which the watch case is made, and the case is covered with a thin layer of gold on top of it. This coating is different high degree resistance to scratches and wear.
- a device for measuring time, showing the current time in certain intervals (seconds, minutes, hours, etc.).
Based on the principle of operation, watches are divided into atomic, quartz, mechanical, sand, solar, and electric.
The main indicators of a watch are accuracy and duration.
The accuracy of the watch is determined by the change in the watch readings compared to the standard (exemplary watch) at a temperature of 20 ±5° for a certain period of time. The average accuracy varies within the following range: for mechanical balance clocks from ±10 seconds to ±120 seconds per day, for household pendulum clocks up to ±30 seconds per week and for electric ones up to ±5-10 seconds per day.
Mechanical watch. The operating principle of the clock mechanism of a mechanical watch is the oscillatory movement of the regulator, which spends a strictly defined period of time on each movement. The duration of the oscillatory movements of the regulator is summed up by a counting mechanism, indicating the process of accumulation of the number of oscillations by arrows moving along the dial.
Based on the type of regulator, mechanical watches are divided into balance and pendulum.
Mechanical watches

Mechanical balance watch
Mechanical balance watches have a regulator in the form of a strictly balanced wheel and a thin spiral spring (the so-called hair). A special feature of mechanical balance watches is their ability to operate reliably in any position with relative accuracy.
A watch consists of a motor, a gear, an escapement, a regulator (balance) with a hair, a winding, transfer and pointer mechanism, and in some brands of mechanical watches, a number of additional devices. The external design details of a mechanical watch include the case, dial and hands.
The engine in a mechanical balance watch is an S-shaped spiral spring, made of carbon or stainless steel. The spring can be open or closed (placed in a drum). The closed spring is used in all pocket and wrist watches, as well as in best examples wall and tabletop. Closed springs have a higher coefficient useful action, better retain lubricant and protect the spring from dust and dirt. Mechanical watches are wound by twisting the spring using a shaft-rotating winding mechanism. A gear system transmits movement from the spring to the hands and balance. The gear train is designed so that the hands move at different speeds and can show the current time in seconds, minutes, hours or longer periods of time.
The supports (stones) of the most critical axes of the gear transmission, escapement and balance to reduce friction and wear of parts and thereby ensure better adjustment, durability of the watch and stability of its movement are made of synthetic ruby and their number in mechanical balance watches of the USSR ranged from 4 to 22 or more.
Hour stones

Hour stones: 1 - through; 2 - invoice; 3 - pallet; 4 - ellipse
The number of stones is one of the indicators of the quality of a mechanical balance watch.
Here is an approximate placement of stones in a 15-jewel balance watch:
2 overhead balance axis
2 through balance axis
2 through axle anchor fork
1 ellipse Balance roller
2 pallets Anchor fork
2 through axle escape wheel
2 through-axis seconds wheel
2 through axle intermediate wheel
In addition, stones can be placed for the axis of the central wheel (1-2 through), for the axis of the anchor wheel (2 overhead), for the axis of the central second hand and for the axes of various additional devices. In watches with fewer stones, the location of the latter may be different, mainly in the balance and anchor fork units.
Kinematic diagram of the pocket watch mechanism

The gear system is connected to the escape wheel, which transmits impulses to the balance through the escape fork. The escape wheel, anchor fork and balance make up the escapement mechanism, the purpose of which is to periodically impart impulses to the balance and convert the free rotational movement of the wheels into a uniformly intermittent one. In hours Soviet Union the descent was made free. With a free anchor descent, the regulator oscillates freely, only momentarily coming into contact with the anchor fork. The anchor fork can be with pallets made of synthetic ruby or steel pins and, depending on them, the escapement can be called pallet or pin. The pallet descent is more reliable and trouble-free in operation, has less energy loss and is subject to negligible wear.
Anchor pallet run

Anchor pallet run: 1 - pallets; 2 - anchor wheel; 3 - balance; 4 anchor fork
The balance with a hair regulates the intermittent, strictly uniform, movement of the gear train and the hands associated with it and largely ensures the average daily accuracy and stability of the watch. The hairs were usually made of an iron-nickel alloy and have increased rigidity, high compensation qualities and practically do not change their elastic properties when the air temperature changes. Most often, pocket and wrist watches used hairs with a so-called end curve (Breguet). The presence of a breguet hair ensures greater accuracy of the watch.
To adjust the rate of the watch, the balance has a special device (thermometer), with which you can increase or decrease the length of the working part of the hair and thereby speed up or slow down the rate of the clock. Marks were placed on the balance bridge or letter designation“—” or “u” (reduce the move) and “+” or “p” (add the move).
Mechanism of the “Pobeda” wristwatch

In order for the action of the spring to be stable and not noticeably weaken by the end of the watch winding period, the complete winding of the watch is designed for a duration slightly longer than the standard winding frequency. Thus, the frequency of winding a watch can be daily, weekly, ten-day, fortnightly, etc., and the validity period of a watch from one full winding is accordingly provided for at least 26, 180, 200, 260 and 360 hours. To maintain the duration of the watch from one full winding, and therefore to make it run more evenly, some brands of wristwatches were produced with a spring winding mechanism using an unbalanced weight. To maintain even movement, it is necessary to wind the watch at the same time.
One of the main indicators of the quality of a watch is its accuracy. The accuracy of the time is determined by the change in the readings of the tested watch with the reference watch at the same temperature. The accuracy of balance mechanical watches can be normal, precision or chronometer. Mechanical balance clocks with normal accuracy allow daily deviations of up to ±120 seconds; precision (accurate; from French precision - accuracy) - up to ±30 seconds and chronometer (especially accurate; from Greek chronos - time and metreo - measure) - up to ±10 seconds. The accuracy of mechanical balance watches depends on the duration of the watch from one complete winding, depending on the presence of the end curve of the hair (braget), the presence of an open or closed spring, as well as its type, the type of trigger (pallet or pin), the accuracy of adjustment, the presence of stones, as well as operating conditions.
Additional devices in mechanical balance wristwatches are anti-magnetic properties, water-resistant casing, calendar, stopwatch and alarm devices, automatic winding, shock-proof and braking devices.
Antimagnetic properties were created by shielding the case (by making it from permaloy or mumetal), using a hair from the nivarox alloy, an anchor fork and a wheel, as well as hands and some other parts made of non-magnetizable materials, such as brass.
Such watches can operate reliably and accurately in a constant magnetic field with an induction of up to 1000 gauss, after which the accuracy and reliability of operation are impaired. Ordinary watches are magnetized already at 30-40 gauss.
Waterproof housing of a wristwatch is ensured by screw-fitting the cover onto a special seal (a gasket made of polyvinyl chloride or other materials) and a sealing gasket around the winding shaft.
Calendar device allows you to display numbers, names of days and months, phases of the moon and some other information. The movement of indicators is carried out by a special mechanism consisting of additional pairs of gear wheels associated with a gear train.
Stopwatch device consists of additional pairs of gears, control levers and hands and allows you to use the watch as a stopwatch, i.e., keep time. They can be with one or two hands and a measured time counter. They have start, stop and return to zero buttons for stopwatch hands.
Signal device allows you to give a sound signal at a predetermined time and, according to the principle of operation, resembles a regular alarm clock. The signal is produced under the action of a special spring by striking a hammer on a pin mounted on a membrane located between the mechanism and the watch cover, or directly on the watch cover itself.
Automatic winding is carried out by an unbalanced weight located under the watch cover and a special mechanism during its operation on the hand. When stationary, the watch does not wind. Automatic watches have better running performance due to the greater stability of the torque of their spring.
Shockproof device allows, in case of a fall or impact of the watch, to protect the thin trunnions of the balance axis and the fragile stones of the balance unit from breaking and ensure continuity precise work hours when they are suddenly shaken. This is achieved by using elastic shock-absorbing supports, allowing the balance axis to move radially and vertically and rest against the stationary parts of the watch not with thin pins, but with thicker and more durable parts.
Braking device makes it possible to stop the watch and thereby set the exact time when the readings of the hour, minute and second hands completely coincide. Stopping the watch is achieved by pulling the crown to the position for moving the hands.
For the blind Pocket and wrist watches were produced, which, instead of a bezel with glass, have a metal cover that flips when pressed, and on the dial near the numbers of the hour scale there are convex dots that allow the blind to determine the time by touch by the position of the hands and dots.
Mechanical balance clocks come in pocket, wrist, wall and table (mantel) watches.
Mechanical balance pocket watches usually have a chrome-plated steel case, round, open, with a glazed dial (organic glass) and a bottom cover with a latch.
Case dimensions range from 40 to 50 mm in diameter. The dial is metal, covered with white or light enamel of other colors, the numbers are printed or applied, the hands are blackened. According to the accuracy of the daily cycle, the following groups were produced.
Chronometer with accuracy of ±10 seconds and duration from one full winding of 42-60 hours.
Precision with an accuracy of ±15 seconds and a duration of action from one full winding of 36 hours.
Normal with accuracy of ±30 seconds. Produced in the early sixties in the following assortment:
“Iskra” - with 17 jewels, the duration of action from one full winding is 32 hours, with a side seconds hand;
“Beam” - with 18 jewels, the duration of action from one full winding is 32 hours, with a side seconds hand;
“Lightning” - on 15 stones, otherwise the same as “Iskra”.
Normal with accuracy ±45 sec. Produced in the following assortment:
28-ChK - with 19 jewels, with a stopwatch device, the duration of action from one full winding is at least 32 hours, with a side seconds hand;
“Zlatoust” (K-43) - with 15 jewels, the duration of action from one full winding is at least 30 hours, with a side seconds hand.
Normal with an accuracy of ±60 sec. Produced in the following assortment:
77-ChK - with 15 jewels, the duration of action from one full winding is at least 32 hours, without a second hand. The front cover also opens with a latch. There are raised dots next to the numbers. Designed for the blind.
Mechanical balance wristwatches are available for women and men.
Women's watches are different from men's sizes and finishing of cases. Wristwatch cases can be round, oval, oblong, square, shaped, etc. The fastening of the lugs for the belt is also the most various shapes. The bottom cover of the watch may be latched or have a bayonet or screw closure. The cases were made of aluminum, nickel silver, stainless steel and gold (583 standard). Aluminum cases can be anodized to match the color of gold, and nickel-silver cases can be nickel-plated, gold-plated and chrome-plated. Women's case sizes range from 16.5 to 28.5 mm in diameter, men's cases from 26.6 to 36.2 mm. The size (caliber) and shape of the watch movement determine the minimum case size. Some wrist Ladies Watch were produced with cases mounted into a bracelet for wearing. The mechanism of watches of different brands and factories may have a number of design features that do not affect the consumer quality parameters of the watch. The color and finish of the dial and hands are varied. Digitization is complete, even or partial, numbers are printed or embossed.
The duration of the watch from one full winding is at least 34 hours. (“Wave” - 42 hours, “Vostok” - 46 hours.). Even with the same indicators, watches may differ in the sizes and shapes of the case, the finishing of the case and dial, digitization, hands, etc.
Mechanical balance women's wristwatches were produced with an accuracy of ±45, ±60 and ±90 seconds.
Watch with accuracy ±45 sec. were produced in the following assortment:
“Star” - on 15 jewels, with a side seconds hand;
“Sura” - with 15 jewels, with a central second hand and a shock-proof device.
Watches with an accuracy of ±60 seconds were produced in the following assortment:
“Aurora” - with 15 jewels, with a central seconds hand and a shock-proof device;
“Spring” - with 17 jewels, with a central seconds hand and a shock-proof device;
“Comet” - with 16 jewels, with a side seconds hand.
Watch with accuracy of ±90 sec. were produced in the following assortment:
“Volga” - with 16 jewels, without a second hand;
“Zarya” - with 16 jewels, without a second hand;
“Era” - on 17 jewels, without a second hand.
Mechanical balance men's wristwatches were produced with precision and normal accuracy of ±30 and ±45 seconds.
Hours from precision accuracy strokes were produced in the following assortment:
“Vostok” - with 22 jewels, in a dust- and moisture-proof case, with a central seconds hand.
Watches with normal accuracy of ±30 seconds were produced in the following assortment:
Mechanical pocket and wrist watches
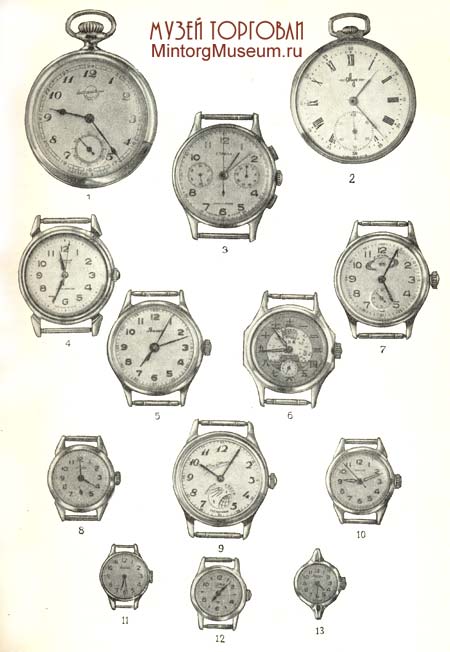
Mechanical pocket and wrist watches: 1 — pocket K-43 (“Zlatoust”); 2 — pocket “Beam”; 3 - men's wristwatch “Strela” (with a stopwatch); 4 - men's wristbands “Motherland”; 5 - men's wristwatches "Volga"; 6 - men's wristbands “Friendship”; 7 - men's wristwatch “Saturn” (with a calendar device); 8 - women’s wrist “Comet”; 9 - men's wrists« Satellite"; 10 - women’s wrist “Spring”; 11 - women's wristwatches "Volga"; 12 - women's wristwatches “Era”; 13 - women's wristwatch "Volga"
Watch for the blind

Watches for the blind: 1 - pocket watch "77-ChK"; 2 - wristwatch "Petrodvorets"
Watch "Chelyabinsk"

Surprisingly good watch. These are the ones that have never broken during their entire existence.
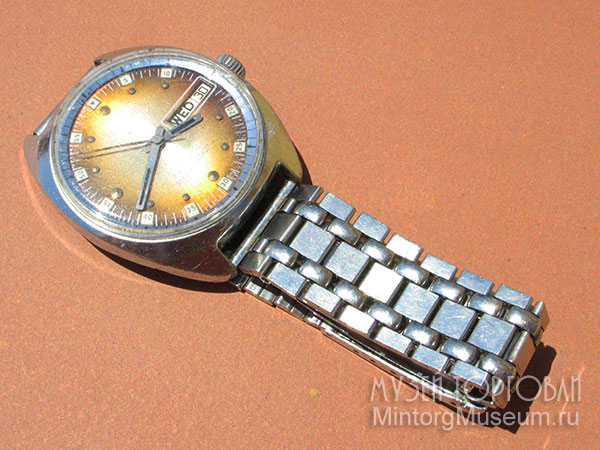

"Cornavin" 27 jewels, automatic, shockproof stainless steel, back waterprotected, USSR
Wristwatch "Cornavin", USSR

Wristwatch "Cornavin", USSR

The external components of a wristwatch include glass, bezel, crown, dial, hands, and case. Each of these elements has gone through many years of development and, although essentially unchanged in essence, has been improved through the use of new materials and manufacturing technologies. But all these parts are still available both in elite Swiss watches and in models offered on street stalls.
The main protector of the dial is glass. The simplest option is made of acrylic. This inexpensive plastic can prevent minor scratches. But mineral glass has more possibilities; its hardness also protects against deep scratches. The most reliable is sapphire glass; it is 20 times heavier than acrylic and 3 times heavier than mineral glass. It is clear that sapphire crystals are installed on expensive watches.
The bezel is the outer ring on the watch located around the crystal. The purpose of the bezel is to hold the glass in place. In sports models it is sometimes used as a component of the watch mechanism. He can move in different directions clockwise and participate in accurate time calculations.
The crown or key of a watch is usually round in shape. For several centuries, it has been used to wind watches and move their hands. Modern models Elite Swiss watches and products from other reputable manufacturers may have crowns screwed down, this characteristic waterproof products.
The dial is considered to be the face of the watch. At the same time, it contains all the necessary information and is the field for placing decor and inlays. Today, manufacturers can offer watches without a traditional dial - skeletons. Their special feature is the clock mechanism that is visible to the eye. Often, on the main dial of luxury Swiss watches there are smaller dials that perform various additional functions.
The shell of the watch is called the case; it houses the mechanism, protecting it from damage. The strength and tightness of the case are important indicators that affect the service life of the watch. Most often it is made of stainless steel, which looks great and does not need coating. Expensive models of elite Swiss watches can be made of silver, titanium, gold, and platinum.
Models at affordable prices can have a body made of brass or copper; gilding or silver plating technology is also used here. To wear a watch on your hand, use bracelets or straps that are made in the same style as the case. Quality leather straps can be made in different colors. Sports models usually available with rubber or plastic straps.




