Small information about Lev N. Lev Nikolaevich and Sofya Andreevna Tolstoy
Leo Tolstoy (1828-1910) is one of the five most widely read writers. His work made Russian literature recognizable abroad. Even if you haven’t read these works, you probably know Natasha Rostova, Pierre Bezukhov and Andrei Bolkonsky at least from films or jokes. The biography of Lev Nikolayevich can be of interest to every person, because the personal life of a famous person is always of interest, and parallels are drawn with his creative activity. Let's try to trace the life path of Leo Tolstoy.
The future classic came from a noble family known since the 14th century. Peter Andreevich Tolstoy, the writer’s paternal ancestor, earned the favor of Peter I by investigating the case of his son, who was suspected of treason. Then Pert Andreevich headed the Secret Chancellery, and his career took off. Nikolai Ilyich, the father of the classic, received a good education. However, it was combined with unshakable principles that did not allow him to advance at court.
The fortune of the father of the future classic was upset due to the debts of his parent, and he married the middle-aged but wealthy Maria Nikolaevna Volkonskaya. Despite the initial calculation, they were happy in marriage and had five children.
Childhood
Lev Nikolaevich was born fourth (there was also the youngest Maria and the elders Nikolai, Sergei and Dmitry), but after his birth he received little attention: his mother died two years after the birth of the writer; the father moved with the children to Moscow for a short time, but soon died too. The impressions from the trip were so strong that young Leva created his first essay, “The Kremlin.”
The children were raised by several guardians at once: first T.A. Ergolskaya and A. M. Osten-Sacken. A. M. Osten-Sacken died in 1840, and the children went to Kazan to live with P. I. Yushkova.
Boyhood
Yushkova’s house was secular and cheerful: receptions, evenings, external splendor, high society - all this was very important for the family. Tolstoy himself sought to shine in society, to be “comme il faut,” but shyness did not allow him to unfold. Real entertainment for Lev Nikolayevich was replaced by reflection and introspection.
The future classicist studied at home: first under the guidance of the German tutor Saint-Thomas, and then with the Frenchman Reselman. Following the example of the brothers, Lev decides to enter the Imperial Kazan University, where Kovalevsky and Lobachevsky worked. In 1844, Tolstoy began studying at the Faculty of Oriental Studies (the admissions committee was amazed by his knowledge of the “Turkish-Tatar language”), and later transferred to the Faculty of Law.
Youth
The young man had a conflict with his home history teacher, so the grades in the subject were unsatisfactory, and he had to take the course again at the university. In order to avoid repeating what had happened, Lev switched to law school, but did not finish, left the university and went to Yasnaya Polyana, his parents’ estate. Here he is trying to run a household using new technologies, he tried, but was unsuccessful. In 1849, the writer went to Moscow.
During this period, keeping a diary begins; entries will continue until the death of the writer. They are the most important document; in Lev Nikolaevich’s diaries he describes the events of his life, and engages in introspection, and reasons. It also described the goals and rules that he tried to follow.
History of success
The creative world of Leo Tolstoy took shape in his adolescence, in his emerging need for constant psychoanalysis. Systematically, this quality was manifested in diary entries. It was as a result of constant self-analysis that Tolstoy’s famous “dialectics of the soul” appeared.
First works
The children's work was written in Moscow, and the real works were also written there. Tolstoy creates stories about gypsies, about his daily routine (unfinished manuscripts have been lost). In the early 50s, the story “Childhood” was also written.
Leo Tolstoy – participant in the Caucasian and Crimean wars. Military service gave the writer many new plots and emotions, described in the stories “Raid”, “Cutting Wood”, “Demoted”, and in the story “Cossacks”. “Childhood”, which brought fame, was also completed here. Impressions from the battle for Sevastopol helped write the cycle “Sevastopol Stories”. But in 1856, Lev Nikolaevich left the service forever. The personal history of Leo Tolstoy taught him a lot: having seen enough bloodshed in the war, he realized the importance of peace and true values - family, marriage, his people. It is these thoughts that he will subsequently put into his works.
Confession
The story “Childhood” was created in the winter of 1850-51, and published a year later. This work and its sequels “Adolescence” (1854), “Youth” (1857) and “Youth” (never written) were supposed to form the novel “Four Epochs of Development” about the spiritual formation of man.
The trilogies tell about the life of Nikolenka Irtenyev. He has parents, an older brother Volodya and a sister Lyubochka, he is happy in his home world, but suddenly his father announces his decision to move to Moscow, Nikolenka and Volodya go with him. Their mother dies just as unexpectedly. A severe blow of fate ends childhood. In adolescence, the hero conflicts with others and with himself, trying to comprehend himself in this world. Nikolenka’s grandmother dies, he not only grieves for her, but also bitterly notes that some people only care about her inheritance. During the same period, the hero begins to prepare for university and meets Dmitry Nekhlyudov. Having entered the university, he feels like an adult and rushes into the pool of secular pleasures. This pastime does not leave time for study, the hero fails his exams. This event led him to the idea that the chosen path was wrong, leading to self-improvement.
Personal life
It is always difficult for the families of writers: a creative person may not be able to live in everyday life, and besides, he always has no time for earthly things, he is overwhelmed by new ideas. What was life like for Leo Tolstoy’s family?
Wife
Sofya Andreevna Bers was born into a doctor's family, she was smart, educated, simple. The writer met his future wife when he was 34 and she was 18. The clear, bright and pure girl attracted the experienced Lev Nikolaevich, who had already seen a lot and was ashamed of his past.
After the wedding, the Tolstoys began to live in Yasnaya Polyana, where Sofya Andreevna took care of the house, children and helped her husband in all matters: she rewrote manuscripts, published works, was a secretary and translator. After the opening of a hospital in Yasnaya Polyana, she helped there too, examining patients. Tolstoy’s family relied on her care, because it was she who carried out all the economic activities.
During a spiritual crisis, Tolstoy came up with a special charter of life and decided to renounce his property, depriving his children of his fortune. Sofya Andreevna opposed this, family life began to crack. However, Lev Nikolaevich has only one wife, and she made a great contribution to his work. He had an ambivalent attitude towards her: on the one hand, he respected and idolized her, on the other, he blamed her for being more involved in material matters than spiritual ones. This conflict was continued in his prose. For example, in the novel “War and Peace” the surname of the negative hero, angry, indifferent and obsessed with hoarding, is Berg, which is very similar to his wife’s maiden name.
Children
Leo Tolstoy had 13 children, 9 boys and 4 girls, but five of them died in childhood. The image of the great father lived in his children, all of them were connected with his work.
Sergei was involved in his father’s work (he founded a museum, commented on works), and also became a professor at the Moscow Conservatory. Tatyana was a follower of her father's teachings and also became a writer. Ilya led a chaotic life: he dropped out of school, did not find a suitable job, and after the revolution he emigrated to the USA, where he lectured on the worldview of Lev Nikolaevich. Leo, too, at first followed the ideas of Tolstoyism, but later became a monarchist, so he also emigrated and was engaged in creativity. Maria shared her father’s ideas, abandoned the light and was engaged in educational work. Andrei highly valued his noble origins, participated in the Russian-Japanese War, then stole his wife from his boss, and soon died suddenly. Mikhail was musical, but became a military man and wrote memoirs about life in Yasnaya Polyana. Alexandra helped her father in all matters, then became the keeper of his museum, but due to emigration, they tried to forget her achievements in Soviet times.
Creative crisis
In the second half of the 60s and early 70s, Tolstoy experienced a painful spiritual crisis. For several years the writer was accompanied by panic attacks, thoughts of suicide, and fear of death. Lev Nikolaevich could not find the answer to the questions of existence that tormented him anywhere, and he created his own philosophical teaching.
Change of worldview
The path to victory over the crisis was unusual: Leo Tolstoy created his own moral teaching. His thoughts were expressed in books and articles: “Confession”, “So what should we do”, “What is art”, “I cannot remain silent”.
The writer’s teaching was anti-Orthodox in nature, since Orthodoxy, according to Lev Nikolaevich, distorted the essence of the commandments, its dogmas are not acceptable from a moral point of view, and were imposed by centuries-old traditions forcibly instilled in the Russian people. Tolstoyism found a response among the common people and the intelligentsia; pilgrims from different classes began to come to Yasnaya Polyana for advice. The Church reacted sharply to the spread of Tolstoyism: in 1901 the writer was excommunicated from it.
Tolstoyism
Morality, ethics and philosophy are combined in Tolstoy's teachings. God is the best in man, his moral center. That is why one cannot follow dogma and justify any violence (which the Church did, according to the author of the teaching). The brotherhood of all people and victory over world evil are the ultimate goals of humanity, which can be achieved through self-improvement of each of us.
Lev Nikolaevich took a different look not only at his personal life, but also at his work. Only the common people are close to the truth, and art should only separate good and evil. And this role is fulfilled by folk art alone. This leads Tolstoy to abandon his past works and simplify his new works as much as possible with the addition of edifying content (“Kholstomer”, “The Death of Ivan Ilyich”, “The Master and the Worker”, “Resurrection”).
Death
Since the beginning of the 80s, family relations have become strained: the writer wants to give up the copyright on his books, his property and give everything to the poor. The wife sharply opposed it, promising to accuse her husband of being crazy. Tolstoy realized that the problem could not be solved peacefully, so he decided to leave his home, go abroad and become a peasant.
Accompanied by Dr. D.P. Makovitsky, the writer left the estate (later his daughter Alexandra joined). However, the writer’s plans were not destined to come true. Tolstoy had a fever and stopped at the head of the Astapovo station. After ten days of illness, the writer died.
Creative heritage
Researchers distinguish three periods in the work of Leo Tolstoy:
- Creativity of the 50s (“young Tolstoy”)- during this period, the writer’s style, his famous “dialectic of the soul” takes shape, he accumulates impressions, military service also helps with this.
- Creativity of the 60s-70s (classical period)– it was at this time that the writer’s most famous works were written.
- 1880-1910 (Tolstoyan period)- bear the imprint of a spiritual revolution: renunciation of past creativity, new spiritual principles and problems. The style is simplified, as are the plots of the works.
November 20 (November 7, old style) marks exactly one hundred years since the death of the Russian writer Leo Nikolaevich Tolstoy.
The great Russian writer, playwright, publicist, Count Lev Nikolaevich Tolstoy was born on September 9 (August 28, old style) 1828 in the Yasnaya Polyana estate of the Krapivensky district of the Tula province (now Shchekinsky district of the Tula region) into one of the most notable Russian noble families. He was the fourth child in the family. The future writer spent his childhood in Yasnaya Polyana. He was orphaned early, losing first his mother, who died when the boy was two years old, and then his father.
In 1837, the family moved from Yasnaya Polyana to Moscow. The guardian of the orphaned children was their aunt, their father’s sister Alexandra Ilyinichna Osten-Saken. In 1841, after her death, young Tolstoy with his sister and three brothers moved to Kazan, where another aunt lived, Pelageya Ilyinichna Yushkova, who became their guardian.
Tolstoy spent his youth in Kazan. In 1844, he entered Kazan University at the Department of Oriental Languages of the Faculty of Philosophy, then transferred to the Faculty of Law, where he studied for less than two years: his studies did not arouse his interest and he indulged in secular entertainment. In the spring of 1847, disappointed in his university education, he submitted a request for dismissal from the university “due to poor health and domestic circumstances” and left for Yasnaya Polyana, which he received as property under the division of his father’s inheritance.
In Yasnaya Polyana, Tolstoy engaged in self-education; tried to reorganize the life of the peasants, however, disappointed by the unsuccessful management experience, in the fall of 1847 he first went to Moscow, where he led a social life, and in the spring of 1849 he went to St. Petersburg to take exams at the university for the degree of candidate of law. His lifestyle during this period often changed: either he was preparing and passing exams, then he was passionately devoted to music, then he intended to begin an official career, having decided in the fall of 1849 to serve as a clerical employee in the Tula Noble Deputy Assembly, then he dreamed of joining a horse guards regiment as a cadet. Tolstoy's religious sentiments during this period, reaching the point of asceticism, alternated with revelry, cards, and trips to the gypsies. In the family he was considered “the most trifling fellow,” and he was able to repay the debts he incurred then only many years later. However, it was during these years that he developed a serious desire to write and his first unfinished artistic sketches appeared.
In the spring of 1851, on the advice of his older brother Nikolai, Lev Nikolaevich entered military service in the Caucasus. In the fall of 1851, he became a cadet of the 4th battery of the 20th artillery brigade, and then, having passed the junior officer rank exam, became an officer.
In 1851-1853, Tolstoy took part in military operations in the Caucasus (first as a volunteer, then as an artillery officer), and in 1854 he went to the Danube Army. Soon after the start of the Crimean War, at his personal request, he was transferred to Sevastopol.
From November 1854 to August 1855 he took part in the defense of Sevastopol (in the besieged city he fought on the famous 4th bastion). He was awarded the Order of Anna and medals “For the Defense of Sevastopol” and “In Memory of the War of 1853-1856.” More than once he was nominated for the military Cross of St. George, but he never received the “George”.
The writer's impressions of the Caucasian War were reflected in the stories "Raid" (1853), "Cutting Wood" (1855), "Demoted" (1856), in the story "Cossacks" (1852 -1863), artistic essays "Sevastopol in December" (1855 ), "Sevastopol in May" (1855) and "Sevastopol in August 1855" (1856). These essays, called “Sevastopol Stories,” made a huge impression on Russian society. In the Caucasus, the story “Childhood” was completed, which was published under the title “The History of My Childhood” in the magazine “Sovremennik” in 1852 and brought Tolstoy great success and fame as one of the most talented Russian writers. Two years later, a continuation appeared in Sovremennik - the story "Adolescence", and in 1857 the story "Youth" was published.
In November 1855, Tolstoy arrived in St. Petersburg and immediately joined the Sovremennik circle (Nikolai Nekrasov, Ivan Turgenev, Alexey Ostrovsky, Ivan Goncharov, etc.).
In the fall of 1856, Leo Tolstoy, having retired with the rank of lieutenant, left for Yasnaya Polyana, and at the beginning of 1857 he went abroad. He visited France, Italy, Switzerland, Germany (Swiss impressions are reflected in the story “Lucerne”), in the fall he returned to Moscow, then to Yasnaya Polyana, where he began improving schools.
In 1859, he opened a school for peasant children in Yasnaya Polyana, and then helped open more than 20 schools in the surrounding villages. To direct their activities along the right path, from his point of view, he published the pedagogical magazine Yasnaya Polyana (1862). Tolstoy wrote eleven articles about school and pedagogy (“On Public Education”, “Upbringing and Education”, “On Social Activities in the Field of Public Education”, etc.).
In order to study the organization of school affairs in foreign countries, the writer went abroad for the second time in 1860.
In May 1861 (the year of the abolition of serfdom) he returned to Yasnaya Polyana, where, having accepted the position of peace mediator, he actively defended the interests of the peasants, resolving their disputes with the landowners about land. Soon the Tula nobility, dissatisfied with his actions, demanded his removal from office, and in 1862 the Senate issued a decree dismissing Tolstoy. Secret surveillance of him began from Section III.
In the summer of 1862, after a police search, Tolstoy had to close the Yasnaya Polyana school and stop publishing a pedagogical magazine. The reason was the authorities' suspicions that students teaching at the school were engaged in anti-government activities.
In September 1862, Tolstoy married the daughter of a Moscow doctor, Sofya Andreevna Bers, and immediately after the wedding, he took his wife from Moscow to Yasnaya Polyana, where he devoted himself entirely to family life and household concerns. During their 17 years of marriage, they had 13 children.
From the autumn of 1863 to 1869, Leo Tolstoy worked on the novel War and Peace.
In the early 1870s, the writer was again fascinated by pedagogy and he created “ABC” and “New ABC” and compiled a “Book for Reading”, where he included many of his stories.
In the spring of 1873, Tolstoy began and four years later finished work on a great novel about modernity, calling it after the name of the main character - Anna Karenina.
The spiritual crisis experienced by Tolstoy in the late 1870s and early 1880s culminated in a turning point in his worldview. In "Confession" (1879-1882), the writer talks about a revolution in his views, the meaning of which he saw in a break with the ideology of the noble class and a transition to the side of the "simple working people."
In the early 1880s, the Tolstoy family moved to Moscow to educate their growing children. From this time on, Tolstoy spent winters in Moscow.
In the 1880s, Tolstoy's stories "The Death of Ivan Ilyich" and "Kholstomer" ("The Story of a Horse"), "The Kreutzer Sonata", the story "The Devil", the story "Father Sergius" appeared.
In 1882, he took part in the census of the Moscow population and became closely acquainted with the life of the inhabitants of the city slums, which he described in the treatise “So what should we do?” (1882-1886).
In simplification, in likening himself to people from the people, Tolstoy saw the purpose and duty of nobles, intellectuals - everyone who is part of the privileged classes. During this period, the writer comes to a complete denial of his previous literary activity, engages in physical labor, plows, sews boots, and switches to vegetarian food.
In the 1880s, a conflict arose between Tolstoy and Sofya Andreevna over property and income from publishing the writer’s works. On May 21, 1883, he granted his wife full power of attorney to manage all property affairs, and two years later he divided all his property between his wife, sons and daughters. He wanted to distribute all his property to the needy, but he was stopped by his wife’s threat to declare him crazy and establish guardianship over him. Sofya Andreevna defended the interests and well-being of the family and children. Tolstoy granted all publishers the right to freely publish all his works published after 1881 (Tolstoy considered this year to be the year of his own moral turning point). But Sofya Andreevna demanded the privilege for herself to publish her husband’s collected works. In the relationship between Tolstoy and his wife and sons, mutual alienation is growing.
The writer’s new worldview is also reflected in his articles “On the census in Moscow”, “On hunger”, “What is art?”, “Slavery of our time”, “On Shakespeare and drama”, “I cannot remain silent”. In these and subsequent years, Tolstoy also wrote religious and philosophical works: “Criticism of Dogmatic Theology”, “What is My Faith?”, “Connection, Translation and Study of the Four Gospels”, “The Kingdom of God is Within You”. In them, the writer not only showed a change in his religious and moral views, but also subjected to a critical revision of the main dogmas and principles of the teaching of the official church.
Social, religious and philosophical quests led Tolstoy to the creation of his own religious and philosophical system (Tolstoyism). Tolstoy preached in his life and works of art the need for moral improvement, universal love, non-resistance to evil through violence, for which he was attacked both by revolutionary democratic figures and by the church. At the beginning of 1900, he wrote a series of articles exposing the entire system of public administration. The government of Nicholas II issues a resolution according to which the Holy Synod (the highest church institution in Russia) in February 1901 excommunicates Tolstoy from the Orthodox Church as a “heretic.”
In 1901, the writer lived in Crimea, recovering from a serious illness.
In the last decade of his life, he wrote the story "Hadji Murat", the plays "The Living Corpse", "The Power of Darkness", "The Fruits of Enlightenment", the stories "After the Ball", "For What?", and the novel "Sunday".
In the last years of his life, Tolstoy found himself at the center of intrigue and contention between the “Tolstoyites,” on the one hand, and his wife, who defended the well-being of her family and children, on the other.
On July 22, 1910, Tolstoy drew up a will in which he granted all publishers the right to publish his works - both those written after 1881 and earlier. The new will strained relations with his wife.
On November 10 (October 28, old style), 1910, at five o’clock in the morning, Leo Tolstoy, accompanied only by his personal physician Dushan Makovitsky, left Yasnaya Polyana secretly from his family. On the way, Tolstoy fell ill, his temperature rose and he was forced to get off the train en route to Rostov-on-Don. At the small Astapovo railway station of the Ryazan-Ural Railway, in the house of the station master, the writer spent the last seven days of his life. Doctors diagnosed pneumonia.
On November 20 (November 7, old style), 1910, at Astapovo station (now Lev Tolstoy station), Lev Nikolaevich Tolstoy died. His funeral in Yasnaya Polyana became a nationwide event.
The material was prepared based on information from open sources
Lev Nikolaevich Tolstoy. Born on August 28 (September 9), 1828 in Yasnaya Polyana, Tula province, Russian Empire - died on November 7 (20), 1910 at Astapovo station, Ryazan province. One of the most widely known Russian writers and thinkers, revered as one of the world's greatest writers. Participant in the defense of Sevastopol. An educator, publicist, religious thinker, his authoritative opinion caused the emergence of a new religious and moral movement - Tolstoyism. Corresponding member of the Imperial Academy of Sciences (1873), honorary academician in the category of fine literature (1900).
A writer who was recognized during his lifetime as the head of Russian literature. The work of Leo Tolstoy marked a new stage in Russian and world realism, acting as a bridge between the classic novel of the 19th century and the literature of the 20th century. Leo Tolstoy had a strong influence on the evolution of European humanism, as well as on the development of realistic traditions in world literature. The works of Leo Tolstoy have been filmed and staged many times in the USSR and abroad; his plays have been staged on stages all over the world.
The most famous works of Tolstoy are the novels “War and Peace”, “Anna Karenina”, “Resurrection”, the autobiographical trilogy “Childhood”, “Adolescence”, “Youth”, the stories “Cossacks”, “The Death of Ivan Ilyich”, “Kreutzerova” sonata”, “Hadji Murat”, a series of essays “Sevastopol Stories”, dramas “The Living Corpse” and “The Power of Darkness”, autobiographical religious and philosophical works “Confession” and “What is my faith?” and etc..
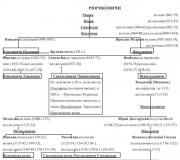
He came from the noble Tolstoy family, known since 1351. The features of Ilya Andreevich’s grandfather are given in “War and Peace” to the good-natured, impractical old Count Rostov. The son of Ilya Andreevich, Nikolai Ilyich Tolstoy (1794-1837), was the father of Lev Nikolaevich. In some character traits and biographical facts, he was similar to Nikolenka’s father in “Childhood” and “Adolescence” and partly to Nikolai Rostov in “War and Peace.” However, in real life, Nikolai Ilyich differed from Nikolai Rostov not only in his good education, but also in his convictions, which did not allow him to serve under Nicholas I.
A participant in the foreign campaign of the Russian army against, including participating in the “Battle of the Nations” near Leipzig and was captured by the French, but was able to escape, after the conclusion of peace he retired with the rank of lieutenant colonel of the Pavlograd Hussar Regiment. Soon after his resignation, he was forced to go into bureaucratic service in order not to end up in debtor's prison because of the debts of his father, the Kazan governor, who died under investigation for official abuses. The negative example of his father helped Nikolai Ilyich develop his ideal of life - a private, independent life with family joys. To put his upset affairs in order, Nikolai Ilyich (like Nikolai Rostov) married the no longer very young Princess Maria Nikolaevna from the Volkonsky family in 1822, the marriage was happy. They had five children: Nikolai (1823-1860), Sergei (1826-1904), Dmitry (1827-1856), Lev, Maria (1830-1912).
Tolstoy's maternal grandfather, Catherine's general, Nikolai Sergeevich Volkonsky, bore some resemblance to the stern rigorist old Prince Bolkonsky in War and Peace. Lev Nikolayevich's mother, similar in some respects to Princess Marya depicted in War and Peace, had a remarkable gift as a storyteller.
In addition to the Volkonskys, L.N. Tolstoy was closely related to several other aristocratic families: the princes Gorchakovs, Trubetskoys and others.
Leo Tolstoy was born on August 28, 1828 in the Krapivensky district of the Tula province, on his mother’s hereditary estate - Yasnaya Polyana. He was the fourth child in the family. The mother died in 1830, six months after the birth of her daughter, from “childbirth fever,” as they said then, when Leo was not yet 2 years old.
A distant relative, T. A. Ergolskaya, took up the task of raising orphaned children. In 1837, the family moved to Moscow, settling on Plyushchikha, as the eldest son had to prepare to enter the university. Soon, the father, Nikolai Ilyich, suddenly died, leaving affairs (including some litigation related to the family’s property) in an unfinished state, and the three youngest children again settled in Yasnaya Polyana under the supervision of Ergolskaya and their paternal aunt, Countess A. M. Osten-Sacken , appointed guardian of the children. Here Lev Nikolaevich remained until 1840, when Countess Osten-Sacken died, and the children moved to Kazan, to a new guardian - their father's sister P. I. Yushkova.
The Yushkov house was considered one of the most fun in Kazan; All family members highly valued external shine. " My good aunt,- says Tolstoy, - the purest being, she always said that she would like nothing more for me than for me to have a relationship with a married woman».
Lev Nikolaevich wanted to shine in society, but his natural shyness and lack of external attractiveness hampered him. The most diverse, as Tolstoy himself defines them, “philosophies” about the most important questions of our existence - happiness, death, God, love, eternity - left an imprint on his character in that era of life. What he told in “Adolescence” and “Youth”, in the novel “Resurrection” about the aspirations of Irtenyev and Nekhlyudov for self-improvement, was taken by Tolstoy from the history of his own ascetic attempts of this time. All this, wrote the critic S. A. Vengerov, led to the fact that Tolstoy created, in the words of his story “Adolescence”, “the habit of constant moral analysis, which destroyed the freshness of feeling and clarity of reason”.
His education was initially carried out by the French tutor Saint-Thomas (the prototype of St.-Jérôme in the story “Boyhood”), who replaced the good-natured German Reselman, whom Tolstoy portrayed in the story “Childhood” under the name of Karl Ivanovich.
In 1843, P.I. Yushkova, taking on the role of guardian of her minor nephews (only the eldest, Nikolai, was an adult) and niece, brought them to Kazan. Following the brothers Nikolai, Dmitry and Sergei, Lev decided to enter the Imperial Kazan University, where Lobachevsky worked at the Faculty of Mathematics, and Kovalevsky worked at the Eastern Faculty. On October 3, 1844, Leo Tolstoy was enrolled as a student of the category of Eastern (Arabic-Turkish) literature as a self-paid student - paying for his studies. In the entrance exams, in particular, he showed excellent results in the compulsory “Turkish-Tatar language” for admission. According to the results of the year, he had poor performance in the relevant subjects, did not pass the transition exam and had to re-take the first-year program.
To avoid repeating the course completely, he transferred to law school, where his problems with grades in some subjects continued. The transitional May 1846 exams were passed satisfactorily (received one A, three Bs and four Cs; the average result was three), and Lev Nikolaevich was transferred to the second year. Leo Tolstoy spent less than two years at the Faculty of Law: “Every education imposed by others was always difficult for him, and everything he learned in life, he learned on his own, suddenly, quickly, with intense work.”, writes S. A. Tolstaya in her “Materials for the biography of L. N. Tolstoy.”
In 1904 he recalled: “The first year I...didn’t do anything. In the second year I began studying...there was Professor Meyer, who...gave me a work - comparing Catherine’s “Order” with Esprit des lois (“Spirit of Laws”). ...this work fascinated me, I went to the village, began to read Montesquieu, this reading opened up endless horizons for me; I started reading and left university precisely because I wanted to study.”.
From March 11, 1847, Tolstoy was in the Kazan hospital; on March 17, he began to keep a diary, where, imitating, he set goals and objectives for self-improvement, noted successes and failures in completing these tasks, analyzed his shortcomings and train of thoughts, the motives of his actions. He kept this diary with short breaks throughout his life.
After finishing the treatment, in the spring of 1847, Tolstoy left his studies at the university and went to Yasnaya Polyana, which he inherited under the division.; his activities there are partly described in the work “The Morning of the Landowner”: Tolstoy tried to establish a new relationship with the peasants. His attempt to somehow smooth out the young landowner’s feeling of guilt before the people dates back to the same year when D. V. Grigorovich’s “Anton the Miserable” and the beginning of “Notes of a Hunter” appeared.
In his diary, Tolstoy formulated for himself a large number of life rules and goals, but he managed to follow only a small part of them. Among those who succeeded were serious studies in English, music, and law. In addition, neither his diary nor his letters reflected the beginning of Tolstoy’s involvement in pedagogy and charity, although in 1849 he first opened a school for peasant children. The main teacher was Foka Demidovich, a serf, but Lev Nikolaevich himself often taught classes.
In mid-October 1848, Tolstoy left for Moscow, settling where many of his relatives and acquaintances lived - in the Arbat area. He stayed at Ivanova’s house on Nikolopeskovsky Lane. In Moscow, he was going to begin preparing for the candidate exams, but classes never started. Instead, he was attracted to a completely different side of life - social life. In addition to the passion for social life, In Moscow, in the winter of 1848-1849, Lev Nikolaevich first developed a passion for playing cards. But since he played very recklessly and did not always think through his moves, he often lost.
Having left for St. Petersburg in February 1849, he spent time in carousing with K. A. Islavin- uncle of his future wife ( “My love for Islavin ruined 8 whole months of my life in St. Petersburg”). In the spring, Tolstoy began to take the exam to become a candidate of rights; He passed two exams, from criminal law and criminal proceedings, successfully, but he did not take the third exam and went to the village.
Later he came to Moscow, where he often spent time gambling, which often had a negative impact on his financial situation. During this period of his life, Tolstoy was especially passionately interested in music (he himself played the piano quite well and greatly appreciated his favorite works performed by others). His passion for music prompted him later to write the Kreutzer Sonata.
Tolstoy's favorite composers were Bach, Handel and. The development of Tolstoy’s love for music was also facilitated by the fact that during a trip to St. Petersburg in 1848, he met in a very unsuitable dance class setting with a gifted but lost German musician, whom he later described in the story “Albert.” In 1849, Lev Nikolaevich settled the musician Rudolf in Yasnaya Polyana, with whom he played four hands on the piano. Having become interested in music at that time, he played works by Schumann, Chopin, and Mendelssohn for several hours a day. In the late 1840s, Tolstoy, in collaboration with his friend Zybin, composed a waltz, which in the early 1900s was performed under the composer S.I. Taneyev, who made a musical notation of this musical work (the only one composed by Tolstoy). A lot of time was also spent on carousing, gaming and hunting.
In the winter of 1850-1851. started writing "Childhood". In March 1851 he wrote “The History of Yesterday.” 4 years after he left the university, Lev Nikolayevich’s brother Nikolai, who served in the Caucasus, came to Yasnaya Polyana and invited his younger brother to join military service in the Caucasus. Lev did not immediately agree, until a major loss in Moscow accelerated the final decision. The writer’s biographers note the significant and positive influence of brother Nikolai on the young and inexperienced Leo in everyday affairs. In the absence of his parents, his older brother was his friend and mentor.
To pay off his debts, it was necessary to reduce his expenses to a minimum - and in the spring of 1851, Tolstoy hastily left Moscow for the Caucasus without a specific goal. He soon decided to enlist in military service, but for this he lacked the necessary documents left in Moscow, while waiting for which Tolstoy lived for about five months in Pyatigorsk, in a simple hut. He spent a significant part of his time hunting, in the company of the Cossack Epishka, the prototype of one of the heroes of the story “Cossacks”, who appears there under the name Eroshka.
In the fall of 1851, Tolstoy, having passed the exam in Tiflis, entered the 4th battery of the 20th artillery brigade, stationed in the Cossack village of Starogladovskaya on the banks of the Terek, near Kizlyar, as a cadet. With some changes in details, she is depicted in the story “Cossacks”. The story reproduces a picture of the inner life of a young gentleman who fled from Moscow life. In the Cossack village, Tolstoy began to write again and in July 1852 he sent the first part of the future autobiographical trilogy - “Childhood”, signed only with initials, to the editors of the most popular magazine at that time, Sovremennik. "L. N.T.”. When sending the manuscript to the journal, Leo Tolstoy included a letter that said: “...I look forward to your verdict. He will either encourage me to continue my favorite activities, or force me to burn everything I started.”.
Having received the manuscript of “Childhood,” the editor of Sovremennik immediately recognized its literary value and wrote a kind letter to the author, which had a very encouraging effect on him. In a letter to I. S. Turgenev, Nekrasov noted: “This talent is new and seems reliable”. The manuscript of an as yet unknown author was published in September of the same year. Meanwhile, the novice and inspired author began to continue the tetralogy “Four Epochs of Development”, the last part of which - “Youth” - never took place. He pondered the plot of “The Landowner’s Morning” (the completed story was only a fragment of “The Roman of a Russian Landowner”), “The Raid,” and “The Cossacks.” Published in Sovremennik on September 18, 1852, “Childhood” was extremely successful; After publication, the author immediately began to be ranked among the luminaries of the young literary school, along with I. S. Turgenev, D. V. Grigorovich, Ostrovsky, who already enjoyed great literary fame. Critics Apollo Grigoriev, Annenkov, Druzhinin appreciated the depth of psychological analysis, the seriousness of the author's intentions and the bright salience of realism.
The relatively late start of his career is very characteristic of Tolstoy: he never considered himself a professional writer, understanding professionalism not in the sense of a profession that provides a means of living, but in the sense of the predominance of literary interests. He did not take the interests of literary parties to heart, and was reluctant to talk about literature, preferring to talk about issues of faith, morality, and social relations.
As a cadet, Lev Nikolaevich remained for two years in the Caucasus, where he participated in many skirmishes with the highlanders led by Shamil, and was exposed to the dangers of military Caucasian life. He had the right to the St. George Cross, but in accordance with his convictions, he “gave it” to a fellow soldier, considering that a significant improvement in the conditions of service of a colleague was higher than personal vanity.
With the beginning of the Crimean War, Tolstoy transferred to the Danube Army, participated in the battle of Oltenitsa and the siege of Silistria, and from November 1854 to the end of August 1855 he was in Sevastopol.
For a long time he lived on the 4th bastion, which was often attacked, commanded a battery in the battle of Chernaya, and was during the bombardment during the assault on Malakhov Kurgan. Tolstoy, despite all the everyday hardships and horrors of the siege, at this time wrote the story “Cutting Wood,” which reflected Caucasian impressions, and the first of the three “Sevastopol stories” - “Sevastopol in December 1854.” He sent this story to Sovremennik. It was quickly published and read with interest throughout Russia, making a stunning impression with the picture of horrors that befell the defenders of Sevastopol. The story was noticed by the Russian Emperor; he ordered to take care of the gifted officer.
Even during the life of Emperor Nicholas I, Tolstoy intended to publish, together with artillery officers, a “cheap and popular” magazine “Military Leaflet”, but Tolstoy failed to implement the magazine project: “For the project, my Sovereign Emperor most graciously deigned to allow our articles to be published in Invalid.”, - Tolstoy bitterly ironized about this.
For the defense of Sevastopol, Tolstoy was awarded the Order of St. Anna, 4th degree with the inscription “For courage,” medals “For the defense of Sevastopol 1854-1855” and “In memory of the war of 1853-1856.” Subsequently, he was awarded two medals “In memory of the 50th anniversary of the defense of Sevastopol”: a silver one as a participant in the defense of Sevastopol and a bronze medal as the author of “Sevastopol Stories”.
Tolstoy, enjoying the reputation of a brave officer and surrounded by the brilliance of fame, had every chance of a career. However, his career was spoiled by writing several satirical songs, stylized as soldiers' songs. One of these songs was dedicated to the failure during the battle near the Chernaya River on August 4 (16), 1855, when General Read, misunderstanding the order of the commander-in-chief, attacked Fedyukhin Heights. A song called “Like the fourth, the mountains carried us hard to take away”, which affected a number of important generals, was a huge success. For her, Lev Nikolaevich had to answer to the assistant chief of staff A. A. Yakimakh.
Immediately after the assault on August 27 (September 8), Tolstoy was sent by courier to St. Petersburg, where he completed “Sevastopol in May 1855.” and wrote “Sevastopol in August 1855,” published in the first issue of Sovremennik for 1856 with the author’s full signature. “Sevastopol Stories” finally strengthened his reputation as a representative of a new literary generation, and in November 1856 the writer left military service forever.
In St. Petersburg, the young writer was warmly welcomed in high society salons and literary circles. He became closest friends with I. S. Turgenev, with whom they lived in the same apartment for some time. Turgenev introduced him to the Sovremennik circle, after which Tolstoy established friendly relations with such famous writers as N. A. Nekrasov, I. S. Goncharov, I. I. Panaev, D. V. Grigorovich, A. V. Druzhinin, V. A. Sollogub.
At this time, “Blizzard”, “Two Hussars” were written, “Sevastopol in August” and “Youth” were completed, and the writing of the future “Cossacks” continued.
However, a cheerful and eventful life left a bitter aftertaste in Tolstoy’s soul, and at the same time he began to have a strong discord with the circle of writers close to him. As a result, “people became disgusted with him, and he became disgusted with himself” - and at the beginning of 1857, Tolstoy left St. Petersburg without any regret and went abroad.
On his first trip abroad, he visited Paris, where he was horrified by the cult of Napoleon I (“The idolization of the villain, terrible”), while at the same time he attended balls, museums, and admired the “sense of social freedom.” However, his presence at the guillotine made such a grave impression that Tolstoy left Paris and went to places associated with the French writer and thinker J.-J. Rousseau - to Lake Geneva. In the spring of 1857, I. S. Turgenev described his meetings with Leo Tolstoy in Paris after his sudden departure from St. Petersburg as follows: “Indeed, Paris is not at all in harmony with its spiritual system; He’s a strange person, I’ve never met anyone like him and I don’t quite understand him. A mixture of poet, Calvinist, fanatic, barich - something reminiscent of Rousseau, but more honest than Rousseau - a highly moral and at the same time unsympathetic creature.".
Trips to Western Europe - Germany, France, England, Switzerland, Italy (in 1857 and 1860-1861) made a rather negative impression on him. He expressed his disappointment in the European way of life in the story “Lucerne.” Tolstoy's disappointment was caused by the deep contrast between wealth and poverty, which he was able to see through the magnificent outer veneer of European culture.
Lev Nikolaevich writes the story “Albert”. At the same time, his friends never cease to be amazed at his eccentricities: in his letter to I. S. Turgenev in the fall of 1857, P. V. Annenkov told Tolstoy’s project to plant forests throughout Russia, and in his letter to V. P. Botkin, Leo Tolstoy reported how very happy he was the fact that he did not become only a writer, contrary to Turgenev’s advice. However, in the interval between the first and second trips, the writer continued to work on “Cossacks”, wrote the story “Three Deaths” and the novel “Family Happiness”.
His last novel was published in “Russian Bulletin” by Mikhail Katkov. Tolstoy's collaboration with the Sovremennik magazine, which lasted from 1852, ended in 1859. In the same year, Tolstoy took part in organizing the Literary Fund. But his life was not limited to literary interests: on December 22, 1858, he almost died on a bear hunt.
Around the same time, he began an affair with the peasant woman Aksinya Bazykina, and plans for marriage were brewing.
On his next trip, he was mainly interested in public education and institutions aimed at raising the educational level of the working population. He closely studied issues of public education in Germany and France, both theoretically and practically - in conversations with specialists. Of the outstanding people in Germany, he was most interested in him as the author of the “Black Forest Stories” dedicated to folk life and as a publisher of folk calendars. Tolstoy paid him a visit and tried to get closer to him. In addition, he also met with the German teacher Disterweg. During his stay in Brussels, Tolstoy met Proudhon and Lelewell. I visited London and attended a lecture.
Tolstoy’s serious mood during his second trip to the south of France was also facilitated by the fact that his beloved brother Nikolai died of tuberculosis almost in his hands. The death of his brother made a huge impression on Tolstoy.
Gradually, criticism cooled towards Leo Tolstoy for 10-12 years, until the very appearance of “War and Peace”, and he himself did not strive for rapprochement with writers, making an exception only for. One of the reasons for this alienation was the quarrel between Leo Tolstoy and Turgenev, which occurred while both prose writers were visiting Fet on the Stepanovka estate in May 1861. The quarrel almost ended in a duel and ruined the relationship between the writers for 17 long years.
In May 1862, Lev Nikolaevich, suffering from depression, on the recommendation of doctors, went to the Bashkir farm of Karalyk, Samara province, to be treated with a new and fashionable method of kumis treatment at that time. Initially, he was going to stay in Postnikov’s kumiss clinic near Samara, but, having learned that many high-ranking officials were supposed to arrive at the same time (secular society, which the young count could not tolerate), he went to the Bashkir nomadic camp of Karalyk, on the Karalyk River, in 130 miles from Samara. There Tolstoy lived in a Bashkir tent (yurt), ate lamb, took sunbathing, drank kumiss, tea, and also had fun with the Bashkirs playing checkers. The first time he stayed there for a month and a half. In 1871, when he had already written War and Peace, he returned there again due to deteriorating health. He wrote about his impressions like this: “The melancholy and indifference have passed, I feel myself returning to the Scythian state, and everything is interesting and new... Much is new and interesting: the Bashkirs, who smell of Herodotus, and Russian peasants, and villages, especially charming in the simplicity and kindness of the people.”.
Fascinated by Karalyk, Tolstoy bought an estate in these places, and already spent the summer of the next year, 1872, with his whole family in it.
In July 1866, Tolstoy appeared at a military court as a defender of Vasil Shabunin, a company clerk stationed near Yasnaya Polyana of the Moscow Infantry Regiment. Shabunin hit the officer, who ordered him to be punished with canes for being drunk. Tolstoy argued that Shabunin was insane, but the court found him guilty and sentenced him to death. Shabunin was shot. This episode made a great impression on Tolstoy, since in this terrible phenomenon he saw the merciless force represented by a state based on violence. On this occasion, he wrote to his friend, publicist P.I. Biryukov: “This incident had much more influence on my entire life than all the seemingly more important events in life: loss or recovery of a condition, success or failure in literature, even the loss of loved ones.”.
During the first 12 years after his marriage, he created War and Peace and Anna Karenina. At the turn of this second era of Tolstoy’s literary life stands “Cossacks,” conceived back in 1852 and completed in 1861-1862, the first of the works in which the talent of the mature Tolstoy was most realized.
The main interest of creativity for Tolstoy manifested itself “in the “history” of characters, in their continuous and complex movement and development.” His goal was to show the individual’s ability for moral growth, improvement, and resistance to the environment, relying on the strength of his own soul.
The release of War and Peace was preceded by work on the novel The Decembrists (1860-1861), to which the author returned several times, but which remained unfinished. And “War and Peace” experienced unprecedented success. An excerpt from the novel entitled "1805" appeared in the Russian Messenger of 1865; in 1868 three of its parts were published, soon followed by the remaining two. The first four volumes of War and Peace quickly sold out, and a second edition was needed, which was released in October 1868. The fifth and sixth volumes of the novel were published in one edition, printed in an already increased edition.
"War and Peace" has become a unique phenomenon in both Russian and foreign literature. This work has absorbed all the depth and intimacy of a psychological novel with the scope and diversity of an epic fresco. The writer, according to V. Ya. Lakshin, turned “to a special state of national consciousness in the heroic time of 1812, when people from different segments of the population united in resistance to foreign invasion,” which, in turn, “created the basis for the epic.”
The author showed national Russian traits in the “hidden warmth of patriotism,” in aversion to ostentatious heroism, in a calm faith in justice, in the modest dignity and courage of ordinary soldiers. He portrayed Russia's war with Napoleonic troops as a nationwide war. The epic style of the work is conveyed through the completeness and plasticity of the image, the branching and crossing of destinies, and incomparable pictures of Russian nature.
In Tolstoy's novel, the most diverse layers of society are widely represented, from emperors and kings to soldiers, all ages and all temperaments throughout the reign of Alexander I.
Tolstoy was pleased with his own work, but already in January 1871 he sent a letter to A. A. Fet: “How happy I am... that I will never write verbose rubbish like “War” again”. However, Tolstoy hardly underestimated the importance of his previous creations. When asked by Tokutomi Rock in 1906 which of his works Tolstoy loved most, the writer replied: "Novel "War and Peace"".
In March 1879, in Moscow, Leo Tolstoy met Vasily Petrovich Shchegolenok, and in the same year, at his invitation, he came to Yasnaya Polyana, where he stayed for about a month and a half. The Shchegolenok told Tolstoy many folk tales, epics and legends, of which more than twenty were written down by Tolstoy, and Tolstoy, if he didn’t write them down on paper, remembered the plots of some of them: six works written by Tolstoy have their source in the stories of the Shchegolenok (1881 - “How People Live” , 1885 - “Two Old Men” and “Three Elders”, 1905 - “Korney Vasiliev” and “Prayer”, 1907 - “Old Man in the Church”). In addition, Tolstoy diligently wrote down many sayings, proverbs, individual expressions and words told by the Goldfinch.
Tolstoy’s new worldview was most fully expressed in his works “Confession” (1879-1880, published in 1884) and “What is My Faith?” (1882-1884). Tolstoy dedicated the story “The Kreutzer Sonata” (1887-1889, published in 1891) and “The Devil” (1889-1890, published in 1911) to the theme of the Christian principle of love, devoid of all self-interest and rising above sensual love in the fight against the flesh. In the 1890s, trying to theoretically substantiate his views on art, he wrote the treatise “What is Art?” (1897-1898). But the main artistic work of those years was his novel “Resurrection” (1889-1899), the plot of which was based on a real court case. The sharp criticism of church rituals in this work became one of the reasons for the excommunication of Tolstoy by the Holy Synod from the Orthodox Church in 1901. The highest achievements of the early 1900s were the story “Hadji Murat” and the drama “The Living Corpse”. In “Hadji Murad,” the despotism of Shamil and Nicholas I is equally exposed. In the story, Tolstoy glorified the courage of struggle, the power of resistance and love of life. The play “The Living Corpse” became evidence of Tolstoy’s new artistic quests, which were objectively close to Chekhov’s drama.
At the beginning of his reign, Tolstoy wrote to the emperor with a request to pardon the regicides in the spirit of evangelical forgiveness. Since September 1882, secret surveillance has been established over him to clarify relations with sectarians; in September 1883 he refused to serve as a juror, citing incompatibility with his religious worldview. At the same time, he received a ban on public speaking in connection with the death of Turgenev. Gradually, the ideas of Tolstoyism begin to penetrate society. At the beginning of 1885, a precedent was set in Russia for refusing military service with reference to Tolstoy’s religious beliefs. A significant part of Tolstoy’s views could not receive open expression in Russia and were presented in full only in foreign editions of his religious and social treatises.
There was no unanimity regarding Tolstoy's artistic works written during this period. Thus, in a long series of short stories and legends intended primarily for popular reading (“How People Live,” etc.), Tolstoy, in the opinion of his unconditional admirers, reached the pinnacle of artistic power. At the same time, according to people who reproach Tolstoy for turning from an artist into a preacher, these artistic teachings, written for a specific purpose, were grossly tendentious.

The lofty and terrible truth of “The Death of Ivan Ilyich,” according to fans, placing this work on a par with the main works of Tolstoy’s genius, according to others, is deliberately harsh, it sharply emphasized the soullessness of the upper strata of society in order to show the moral superiority of a simple “kitchen peasant” » Gerasima. “The Kreutzer Sonata” (written in 1887-1889, published in 1890) also aroused opposite reviews - the analysis of marital relations made one forget about the amazing brightness and passion with which this story was written. The work was banned by censorship, but it was published thanks to the efforts of S. A. Tolstoy, who achieved a meeting with Alexander III. As a result, the story was published in a censored form in the Collected Works of Tolstoy with the personal permission of the Tsar. Alexander III was pleased with the story, but the queen was shocked. But the folk drama “The Power of Darkness,” according to Tolstoy’s admirers, became a great manifestation of his artistic power: in the tight framework of an ethnographic reproduction of Russian peasant life, Tolstoy managed to fit so many universal human traits that the drama with tremendous success went around all the stages of the world.
During the famine of 1891-1892. Tolstoy organized institutions to help the hungry and needy in the Ryazan province. He opened 187 canteens, which fed 10 thousand people, as well as several canteens for children, distributed firewood, provided seeds and potatoes for sowing, bought and distributed horses to farmers (almost all farms became horseless during the famine year), and donated Almost 150,000 rubles were collected.
The treatise “The Kingdom of God is within you...” was written by Tolstoy with short breaks for almost 3 years: from July 1890 to May 1893. The treatise aroused the admiration of the critic V.V. Stasov (“the first book of the 19th century”) and I. E. Repin (“this thing of terrifying power”) could not be published in Russia due to censorship, and it was published abroad. The book began to be distributed illegally in huge numbers of copies in Russia. In Russia itself, the first legal publication appeared in July 1906, but even after that it was withdrawn from sale. The treatise was included in the collected works of Tolstoy, published in 1911, after his death.
In his last major work, the novel “Resurrection,” published in 1899, Tolstoy condemned judicial practice and high society life, portrayed the clergy and worship as secularized and united with secular power.
The turning point for him from the teachings of the Orthodox Church was the second half of 1879. In the 1880s, he took a position of unambiguously critical attitude towards church doctrine, the clergy, and official church life. The publication of some of Tolstoy's works was prohibited by both spiritual and secular censorship. In 1899, Tolstoy’s novel “Resurrection” was published, in which the author showed the life of various social strata in contemporary Russia; the clergy were depicted mechanically and hastily performing rituals, and some took the cold and cynical Toporov for a caricature of the Chief Prosecutor of the Holy Synod.
Leo Tolstoy applied his teaching primarily to his own way of life. He denied church interpretations of immortality and rejected church authority; he did not recognize the rights of the state, since it is built (in his opinion) on violence and coercion. He criticized the church teaching, according to which “the life that exists here on earth, with all its joys, beauties, with all the struggle of the mind against darkness, is the life of all the people who lived before me, my whole life with my inner struggle and victories of the mind.” there is not true life, but fallen life, hopelessly spoiled; true, sinless life is in faith, that is, in the imagination, that is, in madness.” Leo Tolstoy did not agree with the teaching of the church that man from his birth, in his essence, is vicious and sinful, since, in his opinion, such a teaching “undercuts at the root everything that is best in human nature.” Seeing how the church was quickly losing its influence on the people, the writer, according to K. N. Lomunov, came to the conclusion: “Everything living is independent of the church.”
In February 1901, the Synod finally decided to publicly condemn Tolstoy and declare him outside the church. Metropolitan Anthony (Vadkovsky) played an active role in this. As it appears in the Chamber-Fourier journals, on February 22, Pobedonostsev visited Nicholas II in the Winter Palace and talked with him for about an hour. Some historians believe that Pobedonostsev came to the Tsar directly from the Synod with a ready-made definition.
In November 1909, he wrote down a thought that indicated his broad understanding of religion: “I do not want to be a Christian, just as I did not advise and would not want there to be Brahmanists, Buddhists, Confucionists, Taoists, Mohammedans and others. We must all find, each in his own faith, what is common to all, and, abandoning what is exclusive, what is our own, cling to what is common.”.
At the end of February 2001, the count's great-grandson Vladimir Tolstoy, manager of the writer's museum-estate in Yasnaya Polyana, sent a letter to Patriarch Alexy II of Moscow and All Rus' with a request to reconsider the synodal definition. In response to the letter, the Moscow Patriarchate stated that the decision to excommunicate Leo Tolstoy from the Church, made exactly 105 years ago, cannot be reviewed, since (according to Church Relations Secretary Mikhail Dudko), it would be wrong in the absence of the person who the action of the ecclesiastical court applies.
On the night of October 28 (November 10), 1910, L. N. Tolstoy, fulfilling his decision to live his last years in accordance with his views, secretly left Yasnaya Polyana forever, accompanied only by his doctor D. P. Makovitsky. At the same time, Tolstoy did not even have a definite plan of action. He began his last journey at Shchekino station. On the same day, having transferred to another train at the Gorbachevo station, I reached the city of Belyov, Tula province, after which, in the same way, but on another train to the Kozelsk station, I hired a coachman and headed to Optina Pustyn, and from there the next day to Shamordinsky monastery, where he met his sister, Maria Nikolaevna Tolstoy. Later, Tolstoy’s daughter Alexandra Lvovna secretly came to Shamordino.
On the morning of October 31 (November 13), L.N. Tolstoy and his entourage set off from Shamordino to Kozelsk, where they boarded train No. 12, Smolensk - Ranenburg, which had already arrived at the station, heading east. There was no time to buy tickets upon boarding; Having reached Belyov, we purchased tickets to the Volovo station, where we intended to transfer to some train heading south. Those accompanying Tolstoy later also testified that the trip had no specific purpose. After the meeting, they decided to go to his niece E. S. Denisenko, in Novocherkassk, where they wanted to try to get foreign passports and then go to Bulgaria; if this fails, go to the Caucasus. However, on the way, L.N. Tolstoy felt worse - the cold turned into lobar pneumonia and the accompanying people were forced to interrupt the trip that same day and take the sick Tolstoy out of the train at the first large station near the settlement. This station was Astapovo (now Leo Tolstoy, Lipetsk region).
The news of Leo Tolstoy's illness caused a great stir both in high circles and among members of the Holy Synod. Encrypted telegrams were systematically sent to the Ministry of Internal Affairs and the Moscow Gendarmerie Directorate of Railways about his state of health and the state of affairs. An emergency secret meeting of the Synod was convened, at which, on the initiative of Chief Prosecutor Lukyanov, the question was raised about the attitude of the church in the event of a sad outcome of Lev Nikolaevich’s illness. But the issue was never resolved positively.
Six doctors tried to save Lev Nikolaevich, but to their offers to help, he only replied: “God will arrange everything.” When they asked him what he himself wanted, he said: “I want no one to bother me.” His last meaningful words, which he uttered a few hours before his death to his eldest son, which he was unable to understand due to excitement, but which were heard by the doctor Makovitsky, were: “Seryozha... the truth... I love a lot, I love everyone...”.
On November 7 (20), at 6:55 a.m., after a week of severe and painful illness (he was suffocating), Lev Nikolaevich Tolstoy died in the house of the station chief, I. I. Ozolin.
When L.N. Tolstoy came to Optina Pustyn before his death, Elder Barsanuphius was the abbot of the monastery and the monastery commander. Tolstoy did not dare to enter the monastery, and the elder followed him to the Astapovo station to give him the opportunity to reconcile with the Church. But he was not allowed to see the writer, just as his wife and some of his closest relatives from among the Orthodox believers were not allowed to see him.
On November 9, 1910, several thousand people gathered in Yasnaya Polyana for the funeral of Leo Tolstoy. Among those gathered were the writer's friends and admirers of his work, local peasants and Moscow students, as well as government officials and local police sent to Yasnaya Polyana by the authorities, who feared that the farewell ceremony for Tolstoy could be accompanied by anti-government statements, and perhaps even will result in a demonstration. In addition, in Russia this was the first public funeral of a famous person, which was not supposed to take place according to the Orthodox rite (without priests and prayers, without candles and icons), as Tolstoy himself wished. The ceremony was peaceful, as noted in police reports. The mourners, observing complete order, accompanied Tolstoy's coffin from the station to the estate with quiet singing. People lined up and silently entered the room to say goodbye to the body.
On the same day, the newspapers published the resolution of Nicholas II on the report of the Minister of Internal Affairs on the death of Leo Nikolaevich Tolstoy: “I sincerely regret the death of the great writer, who, during the heyday of his talent, embodied in his works the images of one of the glorious times of Russian life. May the Lord God be his merciful judge.".
On November 10 (23), 1910, L. N. Tolstoy was buried in Yasnaya Polyana, on the edge of a ravine in the forest, where as a child he and his brother were looking for a “green stick” that held the “secret” of how to make all people happy. When the coffin with the deceased was lowered into the grave, everyone present reverently knelt.
Family of Leo Tolstoy:
From his youth, Lev Nikolaevich knew Lyubov Alexandrovna Islavina, married to Bers (1826-1886), and loved to play with her children Lisa, Sonya and Tanya. When the Bersov daughters grew up, Lev Nikolaevich thought about marrying his eldest daughter Lisa, he hesitated for a long time until he made a choice in favor of his middle daughter Sophia. Sofya Andreevna agreed when she was 18 years old, and the count was 34 years old, and on September 23, 1862, Lev Nikolaevich married her, having previously admitted his premarital affairs.
For some time, the brightest period begins in his life - he is truly happy, largely thanks to the practicality of his wife, material well-being, outstanding literary creativity and, in connection with it, all-Russian and world-wide fame. In his wife, he found an assistant in all matters, practical and literary - in the absence of a secretary, she rewrote his drafts several times. However, very soon happiness is overshadowed by inevitable minor disagreements, fleeting quarrels, and mutual misunderstandings, which only worsened over the years.
For his family, Leo Tolstoy proposed a certain “life plan”, according to which he proposed giving part of his income to the poor and schools, and significantly simplifying his family’s lifestyle (life, food, clothing), while also selling and distributing “everything extra”: piano, furniture, carriages. His wife, Sofya Andreevna, was clearly not happy with this plan, which is why their first serious conflict broke out and the beginning of her “undeclared war” for a secure future for their children. And in 1892, Tolstoy signed a separate deed and transferred all the property to his wife and children, not wanting to be the owner. Nevertheless, they lived together in great love for almost fifty years.
In addition, his older brother Sergei Nikolaevich Tolstoy was going to marry Sophia Andreevna’s younger sister, Tatyana Bers. But Sergei’s unofficial marriage to the gypsy singer Maria Mikhailovna Shishkina (who had four children from him) made the marriage of Sergei and Tatyana impossible.
In addition, Sofia Andreevna’s father, physician Andrei Gustav (Evstafievich) Bers, even before his marriage to Islavina, had a daughter, Varvara, from Varvara Petrovna Turgeneva, the mother of Ivan Sergeevich Turgenev. On her mother’s side, Varya was the sister of Ivan Turgenev, and on her father’s side, S. A. Tolstoy, thus, together with marriage, Leo Tolstoy acquired a relationship with I. S. Turgenev.
From the marriage of Lev Nikolaevich with Sofia Andreevna, 13 children were born, five of whom died in childhood. Children:
1. Sergei (1863-1947), composer, musicologist.
2. Tatiana (1864-1950). Since 1899 she has been married to Mikhail Sergeevich Sukhotin. In 1917-1923 she was the curator of the Yasnaya Polyana museum-estate. In 1925 she emigrated with her daughter. Daughter Tatyana Mikhailovna Sukhotina-Albertini (1905-1996).
3. Ilya (1866-1933), writer, memoirist. In 1916 he left Russia and went to the USA.
4. Leo (1869-1945), writer, sculptor. In exile in France, Italy, then in Sweden.
5. Maria (1871-1906). Since 1897 she has been married to Nikolai Leonidovich Obolensky (1872-1934). She died of pneumonia. Buried in the village. Kochaki of Krapivensky district (modern Tula region, Shchekinsky district, village of Kochaki).
6. Peter (1872-1873)
7. Nikolai (1874-1875)
8. Varvara (1875-1875)
9. Andrey (1877-1916), official of special assignments under the Tula governor. Participant in the Russian-Japanese War. He died in Petrograd from general blood poisoning.
10. Mikhail (1879-1944). In 1920 he emigrated and lived in Turkey, Yugoslavia, France and Morocco. Died on October 19, 1944 in Morocco.
11. Alexey (1881-1886)
12. Alexandra (1884-1979). At the age of 16 she became her father's assistant. For her participation in the First World War, she was awarded three St. George Crosses and was awarded the rank of colonel. In 1929 she emigrated from the USSR and in 1941 received US citizenship. She died on September 26, 1979 in Valley Cottage, New York.
13. Ivan (1888-1895).
As of 2010, there were a total of more than 350 descendants of Leo Tolstoy (including both living and deceased), living in 25 countries around the world. Most of them are descendants of Lev Lvovich Tolstoy, who had 10 children, the third son of Lev Nikolaevich. Since 2000, once every two years, meetings of the writer’s descendants have been held in Yasnaya Polyana.
Quotes about Leo Tolstoy:
French writer and member of the French Academy Andre Maurois argued that Leo Tolstoy is one of the three greatest writers in the entire history of culture (along with Shakespeare and Balzac).
German writer, Nobel Prize winner in literature Thomas Mann said that the world did not know another artist in whom the epic, Homeric principle would be as strong as Tolstoy’s, and that the elements of the epic and indestructible realism live in his works.
The Indian philosopher and politician spoke of Tolstoy as the most honest man of his time, who never tried to hide the truth or embellish it, fearing neither spiritual nor temporal power, backing up his preaching with deeds and making any sacrifices for the sake of the truth.
The Russian writer and thinker said in 1876 that only Tolstoy shines because, in addition to the poem, he “knows to the smallest accuracy (historical and current) the reality depicted.”
Russian writer and critic Dmitry Merezhkovsky wrote about Tolstoy: “His face is the face of humanity. If the inhabitants of other worlds asked our world: who are you? - humanity could answer by pointing to Tolstoy: here I am.”
The Russian poet spoke of Tolstoy: “Tolstoy is the greatest and only genius of modern Europe, the highest pride of Russia, a man whose one name is fragrance, a writer of great purity and holiness.”
The Russian writer in the English “Lectures on Russian Literature” wrote: “Tolstoy is an unsurpassed Russian prose writer. Leaving aside his predecessors Pushkin and Lermontov, all the great Russian writers can be arranged in the following sequence: the first is Tolstoy, the second is Gogol, the third is Chekhov, the fourth is Turgenev.”
Russian religious philosopher and writer V. V. Rozanov about Tolstoy: “Tolstoy is only a writer, but not a prophet, not a saint, and therefore his teaching does not inspire anyone.”
Famous theologian Alexander Men said that Tolstoy is still the voice of conscience and a living reproach for people who are confident that they live in accordance with moral principles.
Lev Nikolaevich Tolstoy is one of the greatest novelists in the world. He is not only the world's greatest writer, but also a philosopher, religious thinker and educator. You will learn more about all this from this.
But what he really achieved success in was keeping a personal diary. This habit inspired him to write his novels and stories, and also allowed him to form most of his life goals and priorities.
An interesting fact is that this nuance of Tolstoy’s biography (keeping a diary) was a consequence of imitation of the great.
Hobbies and military service
Naturally, Leo Tolstoy had it. He loved music extremely much. His favorite composers were Bach, Handel and Chopin.
From his biography it is clear that sometimes he could play works by Chopin, Mendelssohn and Schumann on the piano for several hours in a row.
It is reliably known that Leo Tolstoy’s elder brother, Nikolai, had a plot against him. big influence. He was a friend and mentor of the future writer.
It was Nikolai who invited his younger brother to join military service in the Caucasus. As a result, Leo Tolstoy became a cadet, and in 1854 he was transferred to Sevastopol, where he participated in the Crimean War until August 1855.
Tolstoy's creativity
During his service, Lev Nikolaevich had quite a lot of free time. During this period, he wrote an autobiographical story “Childhood”, in which he masterfully described the memories of the first years of his life.
This work became an important event for the compilation of his biography.
After this, Leo Tolstoy writes the next story, “Cossacks,” in which he describes his army life in the Caucasus.
Work on this work continued until 1862, and was completed only after serving in the army.
An interesting fact is that Tolstoy did not stop his writing even while participating in the Crimean War.
During this period, the story “Adolescence”, which is a continuation of “Childhood,” as well as “Sevastopol Stories” came out from his pen.
After the end of the Crimean War, Tolstoy left service. Upon arrival home, he already has great fame in the literary field.
His outstanding contemporaries talk about a major acquisition for Russian literature in the person of Tolstoy.
While still young, Tolstoy was distinguished by arrogance and stubbornness, which is clearly visible in his. He refused to belong to any particular school of thought, and once publicly called himself an anarchist, after which he decided to leave for France in 1857.
He soon developed an interest in gambling. But it didn't last long. When he lost all his savings, he had to return home from Europe.
 Leo Tolstoy in his youth
Leo Tolstoy in his youth By the way, a passion for gambling is observed in the biographies of many writers.
Despite all the difficulties, he writes the last, third part of his autobiographical trilogy “Youth”. This happened in the same 1857.
Since 1862, Tolstoy began publishing the pedagogical magazine Yasnaya Polyana, where he himself was the main employee. However, not having the vocation of a publisher, Tolstoy managed to publish only 12 issues.
Leo Tolstoy's family
On September 23, 1862, a sharp turn took place in Tolstoy’s biography: he married Sofya Andreevna Bers, who was the daughter of a doctor. From this marriage 9 sons and 4 daughters were born. Five of the thirteen children died in childhood.
When the wedding took place, Sofya Andreevna was only 18 years old, and Count Tolstoy was 34 years old. An interesting fact is that before his marriage, Tolstoy confessed to his future wife about his premarital affairs.
 Leo Tolstoy with his wife Sofia Andreevna
Leo Tolstoy with his wife Sofia Andreevna For some time, the brightest period began in Tolstoy’s biography.
He is truly happy, largely thanks to the practicality of his wife, material wealth, outstanding literary creativity and, in connection with it, all-Russian and even worldwide fame.
In his wife, Tolstoy found an assistant in all matters, practical and literary. In the absence of the secretary, it was she who rewrote his drafts several times.
However, very soon their happiness is overshadowed by inevitable minor disagreements, fleeting quarrels and mutual misunderstandings, which only worsen over the years.
The fact is that for his family, Leo Tolstoy proposed a kind of “life plan”, according to which he intended to give part of the family income to the poor and schools.
He wanted to significantly simplify his family’s lifestyle (food and clothing), while he intended to sell and distribute “everything unnecessary”: pianos, furniture, carriages.
 Tolstoy with his family at a tea table in the park, 1892, Yasnaya Polyana
Tolstoy with his family at a tea table in the park, 1892, Yasnaya Polyana Naturally, his wife, Sofya Andreevna, was clearly not happy with such an ambiguous plan. Because of this, their first serious conflict broke out, which served as the beginning of an “undeclared war” to ensure the future of their children.
In 1892, Tolstoy signed a separate deed and, not wanting to be the owner, transferred all the property to his wife and children.
It must be said that Tolstoy’s biography is in many ways unusually contradictory precisely because of his relationship with his wife, with whom he lived for 48 years.
Works of Tolstoy
Tolstoy is one of the most prolific writers. His works are large-scale not only in volume, but also in the meanings that he touches on in them.
Tolstoy's most popular works are War and Peace, Anna Karenina and Resurrection.
"War and Peace"
In the 1860s, Lev Nikolaevich Tolstoy and his entire family lived in Yasnaya Polyana. It was here that his most famous novel, War and Peace, was born.
Initially, part of the novel was published in “Russian Bulletin” under the title “1805”.
After 3 years, 3 more chapters appear, thanks to which the novel was completely finished. He was destined to become the most outstanding creative result in Tolstoy's biography.
Both critics and the public debated the work “War and Peace” for a long time. The subject of their disputes was the wars described in the book.
Thoughtful but still fictional characters were also hotly debated.
 Tolstoy in 1868
Tolstoy in 1868 The novel also became interesting because it presented 3 informative satirical essays about the laws of history.
Among all other ideas, Leo Tolstoy tried to convey to the reader that a person’s position in society and the meaning of his life are derivatives of his daily activities.
"Anna Karenina"
After Tolstoy wrote War and Peace, he began work on his second, no less famous novel, Anna Karenina.
The writer contributed many autobiographical essays to it. This can be easily seen by looking at the relationship between Kitty and Levin, the main characters in Anna Karenina.
The work was published in parts between 1873-1877, and was very highly appreciated by both critics and society. Many have noticed that Anna Karenina is practically an autobiography of Tolstoy, written in the third person.
For his next work, Lev Nikolaevich received fabulous fees for those times.
"Resurrection"
In the late 1880s, Tolstoy wrote the novel “Resurrection.” Its plot was based on a true court case. It is in “Resurrection” that the author’s sharp views on church rituals are clearly outlined.
By the way, this work became one of the reasons that led to a complete break between the Orthodox Church and Count Tolstoy.
Tolstoy and religion
Despite the fact that the works described above were a colossal success, it did not bring any joy to the writer.
He was depressed and experienced deep inner emptiness.
In this regard, the next stage in Tolstoy’s biography was a continuous, almost convulsive search for the meaning of life.

Initially, Lev Nikolaevich looked for answers to his questions in the Orthodox Church, but this did not bring him any results.
Over time, he began to criticize in every possible way both the Orthodox Church itself and the Christian religion in general. He began to publish his thoughts on these pressing issues in the publication “Mediator”.
His main position was that Christian teaching is good, but Jesus Christ himself seems to be unnecessary. That is why he decided to make his own translation of the Gospel.
In general, Tolstoy's religious views were extremely complex and confusing. It was some incredible mixture of Christianity and Buddhism, seasoned with various Eastern beliefs.
In 1901, the Holy Governing Synod issued a ruling on Count Leo Tolstoy.
This was a decree that officially announced that Leo Tolstoy was no longer a member of the Orthodox Church, since his publicly expressed beliefs were incompatible with such membership.
The definition of the Holy Synod is sometimes mistakenly interpreted as excommunication (anathema) of Tolstoy from the church.
Copyrights and conflict with my wife
In connection with his new convictions, Leo Tolstoy wanted to give away all his savings and give up his own property in favor of the poor. However, his wife, Sofya Andreevna, expressed a categorical protest in this regard.
In this regard, a major family crisis emerged in Tolstoy’s biography. When Sofya Andreevna found out that her husband had publicly renounced the copyright to all his works (which, in fact, was their main source of income), they began to have fierce conflicts.
From Tolstoy's diary:
“She doesn’t understand, and the children don’t understand when they spend money, that every ruble they live and earn from books is suffering, my shame. It may be a shame, but why weaken the effect that the preaching of the truth could have.”
Of course, it is not difficult to understand Lev Nikolaevich’s wife. After all, they had 9 children, whom he, by and large, left without a livelihood.
Pragmatic, rational and active Sofya Andreevna could not allow this to happen.
Ultimately, Tolstoy drew up a formal will, transferring the rights to his youngest daughter, Alexandra Lvovna, who fully sympathized with his views.
At the same time, an explanatory note was attached to the will that in fact these texts should not become anyone’s property, and V.G. would assume the authority to monitor the processes. Chertkov is a faithful follower and student of Tolstoy, who was supposed to take all the writer’s works, right down to the drafts.
Tolstoy's later work
Tolstoy's later works were realistic fiction, as well as stories filled with moral content.
In 1886, one of Tolstoy’s most famous stories appeared, “The Death of Ivan Ilyich.”
Its main character realizes that he wasted most of his life, and the realization came too late.
In 1898, Lev Nikolaevich wrote an equally famous work, “Father Sergius.” In it, he criticized his own beliefs that appeared to him after his spiritual rebirth.
The rest of the works are devoted to the theme of art. These include the play “The Living Corpse” (1890) and the brilliant story “Hadji Murat” (1904).
In 1903, Tolstoy wrote a short story called “After the Ball.” It was published only in 1911, after the death of the writer.
last years of life
The last years of his biography, Leo Tolstoy was better known as a religious leader and moral authority. His thoughts were aimed at resisting evil using a non-violent method.
During his lifetime, Tolstoy became an idol for the majority. However, despite all his achievements, there were serious flaws in his family life, which became especially aggravated in old age.
 Leo Tolstoy with his grandchildren
Leo Tolstoy with his grandchildren The writer's wife, Sofya Andreevna, did not agree with her husband's views and disliked some of his followers who often came to Yasnaya Polyana.
She said: “How can you love humanity and hate those who are next to you.”
All this could not last long.
In the fall of 1910, Tolstoy, accompanied only by his doctor D.P. Makovitsky leaves Yasnaya Polyana forever. However, he did not have any specific plan of action.
Death of Tolstoy
However, on the way, L.N. Tolstoy felt unwell. First he caught a cold, and then the illness turned into pneumonia, due to which he had to interrupt the trip and take the sick Lev Nikolaevich out of the train at the first large station near the settlement.
This station was Astapovo (now Leo Tolstoy, Lipetsk region).
Rumors about the writer’s illness instantly spread throughout the entire surrounding area and far beyond its borders. Six doctors tried in vain to save the great old man: the disease progressed inexorably.
On November 7, 1910, Lev Nikolaevich Tolstoy died at the age of 83. He was buried in Yasnaya Polyana.
“I sincerely regret the death of the great writer, who, during the heyday of his talent, embodied in his works the images of one of the glorious times of Russian life. May the Lord God be his merciful judge.”
If you liked the biography of Leo Tolstoy, share it on social networks.
If you generally like biographies of great people and just about everything, subscribe to the site IinterestingFakty.org in any convenient way. It's always interesting with us!
Did you like the post? Press any button.
How is the rating calculated?◊ The rating is calculated based on points awarded over the last week
◊ Points are awarded for:
⇒ visiting pages dedicated to the star
⇒voting for a star
⇒ commenting on a star
Biography, life story of Tolstoy Lev Nikolaevich
OriginHe came from a noble family, known, according to legendary sources, since 1351. His paternal ancestor, Count Pyotr Andreevich Tolstoy, is known for his role in the investigation of Tsarevich Alexei Petrovich, for which he was put in charge of the Secret Chancellery. The traits of Pyotr Andreevich’s great-grandson, Ilya Andreevich, are given in “War and Peace” to the good-natured, impractical old Count Rostov. The son of Ilya Andreevich, Nikolai Ilyich Tolstoy (1794-1837), was the father of Lev Nikolaevich. In some character traits and biographical facts, he was similar to Nikolenka’s father in “Childhood” and “Adolescence” and partly to Nikolai Rostov in “War and Peace.” However, in real life, Nikolai Ilyich differed from Nikolai Rostov not only in his good education, but also in his convictions, which did not allow him to serve under Nikolai. A participant in the foreign campaign of the Russian army against Napoleon, including participating in the “Battle of the Nations” near Leipzig and being captured by the French, after the conclusion of peace he retired with the rank of lieutenant colonel of the Pavlograd Hussar Regiment. Soon after his resignation, he was forced to go into bureaucratic service in order not to end up in debtor's prison because of the debts of his father, the Kazan governor, who died under investigation for official abuses. The negative example of his father helped Nikolai Ilyich develop his ideal of life - a private, independent life with family joys. To put his upset affairs in order, Nikolai Ilyich, like Nikolai Rostov, married a no longer very young princess from the Volkonsky family; the marriage was happy. They had four sons: Nikolai, Sergei, Dmitry, Lev and daughter Maria.
Tolstoy's maternal grandfather, Catherine's general, Nikolai Sergeevich Volkonsky, bore some resemblance to the stern rigorist old Prince Bolkonsky in War and Peace. Lev Nikolaevich's mother, similar in some respects to Princess Marya depicted in War and Peace, had a remarkable gift for storytelling.
In addition to the Volkonskys, L.N. Tolstoy was closely related to several other aristocratic families: the princes Gorchakovs, Trubetskoys and others.
CONTINUED BELOW
Childhood
Born on August 28, 1828 in the Krapivensky district of the Tula province, on his mother’s hereditary estate - Yasnaya Polyana. Was the fourth child; he had three older brothers: Nikolai (1823-1860), Sergei (1826-1904) and Dmitry (1827-1856). In 1830, Sister Maria (1830-1912) was born. His mother died with the birth of her last daughter, when he was not yet 2 years old.
A distant relative, T. A. Ergolskaya, took up the task of raising orphaned children. In 1837, the family moved to Moscow, settling on Plyushchikha, because the eldest son had to prepare to enter university, but soon his father suddenly died, leaving affairs (including some related to family property, litigation) in an unfinished state, and the three youngest children again settled in Yasnaya Polyana under the supervision of Ergolskaya and their paternal aunt, Countess A. M. Osten-Sacken, who was appointed guardian of the children. Here Lev Nikolaevich remained until 1840, when Countess Osten-Sacken died, and the children moved to Kazan, to a new guardian - their father's sister P. I. Yushkova.
The Yushkov house was one of the most fun in Kazan; All family members highly valued external shine. “My good aunt,” says Tolstoy, “a pure being, always said that she would want nothing more for me than for me to have a relationship with a married woman.”
He wanted to shine in society, but his natural shyness and lack of external attractiveness hampered him. The most varied, as Tolstoy himself defines them, “philosophies” about the most important questions of our existence - happiness, death, God, love, eternity - painfully tormented him in that era of life. What he told in “Adolescence” and “Youth” about the aspirations of Irtenyev and Nekhlyudov for self-improvement was taken by Tolstoy from the history of his own ascetic attempts of this time. All this led to the fact that Tolstoy developed a “habit of constant moral analysis,” which, as it seemed to him, “destroyed the freshness of feeling and clarity of reason” (“Adolescence”).
Education
His education was first carried out under the guidance of the French tutor Saint-Thomas (Mr. Jerome in Boyhood), who replaced the good-natured German Reselman, whom he portrayed in Childhood under the name Karl Ivanovich.
In 1841, P.I. Yushkova, taking on the role of guardian of her minor nephews (only the eldest, Nikolai, was an adult) and niece, brought them to Kazan. Following the brothers Nikolai, Dmitry and Sergei, Lev decided to enter the Imperial Kazan University, where Lobachevsky worked at the Faculty of Mathematics, and Kovalevsky worked at the Eastern Faculty. On October 3, 1844, Leo Tolstoy was enrolled as a student in the category of oriental literature as a student. In the entrance exams, in particular, he showed excellent results in the “Turkish-Tatar language” required for admission.
Due to a conflict between his family and the teacher of Russian and general history and the history of philosophy, Professor N.A. Ivanov, at the end of the year he had poor performance in the relevant subjects and had to re-take the first-year program. To avoid repeating the course completely, he transferred to the Faculty of Law, where his problems with grades in Russian history and German continued. Leo Tolstoy spent less than two years at the Faculty of Law: “Every education imposed by others was always difficult for him, and everything he learned in life, he learned himself, suddenly, quickly, with intense work,” writes Tolstaya in her “Materials for biography of L.N. Tolstoy." In 1904 he recalled: “ ...for the first year...I did nothing. In the second year I began to study... there was Professor Meyer, who... gave me a work - a comparison of Catherine’s “Order” with Montesquieu’s “Esprit des lois”. ... this work fascinated me, I went to the village, began to read Montesquieu, this reading opened up endless horizons for me; I started reading Rousseau and dropped out of university precisely because I wanted to study».
While in the Kazan hospital, he began to keep a diary, where, imitating, he set goals and rules for self-improvement and noted successes and failures in completing these tasks, analyzed his shortcomings and train of thoughts, the motives of his actions.
In 1845, L.N. Tolstoy had a godson in Kazan. On November 11 (23), according to other sources - November 22 (December 4), 1845, in the Kazan Spaso-Preobrazhensky Monastery, the 18-year-old Jewish cantonist of the Kazan battalions of military cantonists Zalman was baptized under the name Luka Tolstoy (“Zelman”) Kagan, whose godfather was listed in the documents as a student of the Imperial Kazan University, Count L.N. Tolstoy. Before this - on September 25 (October 7), 1845 - his brother, a student at the Imperial Kazan University, Count D. N. Tolstoy became the successor of the 18-year-old Jewish cantonist Nukhim (“Nohim”) Beser, baptized (with the name Nikolai Dmitriev) archimandrite Kazan Assumption (Zilantov) Monastery by Gabriel (V.N. Voskresensky).
Beginning of literary activity
Having dropped out of the university, Tolstoy settled in Yasnaya Polyana in the spring of 1847; his activities there are partly described in “The Landowner’s Morning”: Tolstoy tried to establish a new relationship with the peasants.
His attempt to somehow atone for the guilt of the nobility before the people dates back to the same year when Grigorovich’s “Anton the Miserable” and the beginning of Turgenev’s “Notes of a Hunter” appeared.
In his diary, Tolstoy sets himself a huge number of goals and rules; Only a small number of them were able to follow. Among those who succeeded were serious studies in English, music, and law. In addition, neither the diary nor the letters reflected the beginning of Tolstoy's studies in pedagogy and charity - in 1849 he first opened a school for peasant children. The main teacher was Foka Demidych, a serf, but Lev Nikolaevich himself often taught classes.
Having left for St. Petersburg in February 1849, he spends time in revelry with K. A. Islavin, the uncle of his future wife (“My love for Islavin ruined for me 8 whole months of life in St. Petersburg”); in the spring he began taking the exam to become a candidate of rights; He passed two exams, from criminal law and criminal proceedings, successfully, but he did not take the third exam and went to the village.
Later he came to Moscow, where he often succumbed to his passion for gambling, greatly upsetting his financial affairs. During this period of his life, Tolstoy was especially passionately interested in music (he himself played the piano quite well and greatly appreciated his favorite works performed by others). The author of the “Kreutzer Sonata” drew an exaggerated description in relation to most people of the effect that “passionate” music produces from the sensations excited by the world of sounds in his own soul.
Tolstoy's favorite composers were Handel and. In the late 1840s, Tolstoy, in collaboration with his acquaintance, composed a waltz, which in the early 1900s he performed under the composer Taneev, who made a musical notation of this musical work (the only one composed by Tolstoy).
The development of Tolstoy’s love for music was also facilitated by the fact that during a trip to St. Petersburg in 1848, he met in a very unsuitable dance class setting with a gifted but lost German musician, whom he later described in Alberta. Tolstoy came up with the idea of saving him: he took him to Yasnaya Polyana and played a lot with him. A lot of time was also spent on carousing, gaming and hunting.
In the winter of 1850-1851. started writing "Childhood". In March 1851 he wrote “The History of Yesterday.”
After leaving the university, 4 years passed when Lev Nikolayevich’s brother Nikolai, who served in the Caucasus, came to Yasnaya Polyana and invited his younger brother to join military service in the Caucasus. Lev did not immediately agree, until a major loss in Moscow accelerated the final decision. The writer’s biographers note the significant and positive influence of brother Nikolai on the young and inexperienced Leo in everyday affairs. In the absence of his parents, his older brother was his friend and mentor.
To pay off his debts, it was necessary to reduce his expenses to a minimum - and in the spring of 1851, Tolstoy hastily left Moscow for the Caucasus without a specific goal. Soon he decided to enlist in military service, but obstacles arose in the form of a lack of necessary papers, which were difficult to obtain, and Tolstoy lived for about 5 months in complete solitude in Pyatigorsk, in a simple hut. He spent a significant part of his time hunting, in the company of the Cossack Epishka, the prototype of one of the heroes of the story “Cossacks”, who appears there under the name Eroshka.
In the fall of 1851, Tolstoy, having passed the exam in Tiflis, entered the 4th battery of the 20th artillery brigade, stationed in the Cossack village of Starogladov, on the banks of the Terek, near Kizlyar, as a cadet. With a slight change in details, she is depicted in all her semi-wild originality in “Cossacks”. The same “Cossacks” also convey a picture of the inner life of a young gentleman who fled from Moscow life.
In a remote village, Tolstoy began to write and in 1852 he sent the first part of the future trilogy: “Childhood” to the editors of Sovremennik.
The relatively late start of his career is very characteristic of Tolstoy: he never considered himself a professional writer, understanding professionalism not in the sense of a profession that provides a means of living, but in the sense of the predominance of literary interests. He did not take the interests of literary parties to heart, and was reluctant to talk about literature, preferring to talk about issues of faith, morality, and social relations.
Military career
Having received the manuscript of “Childhood,” the editor of Sovremennik, Nekrasov, immediately recognized its literary value and wrote a kind letter to the author, which had a very encouraging effect on him.
Meanwhile, the encouraged author sets about continuing the tetralogy “Four Epochs of Development,” the last part of which, “Youth,” never materialized. Plans for “The Morning of the Landowner” (the completed story was only a fragment of “The Romance of a Russian Landowner”), “The Raid”, and “The Cossacks” are swarming in his head. “Childhood,” published in Sovremennik on September 18, 1852, signed with the modest initials L.N., was extremely successful; the author immediately began to be ranked among the luminaries of the young literary school, along with Turgenev, Goncharov, Grigorovich, Ostrovsky, who already enjoyed great literary fame. Criticism - Apollo Grigoriev, Annenkov, Druzhinin, Chernyshevsky - appreciated the depth of psychological analysis, the seriousness of the author's intentions, and the bright salience of realism.
Tolstoy remained in the Caucasus for two years, participating in many skirmishes with the mountaineers and being exposed to the dangers of military Caucasian life. He had rights and claims to the St. George Cross, but did not receive it. When the Crimean War broke out at the end of 1853, Tolstoy transferred to the Danube Army, participated in the battle of Oltenitsa and the siege of Silistria, and from November 1854 to the end of August 1855 he was in Sevastopol.
Tolstoy lived for a long time on the dangerous 4th bastion, commanded a battery at the Battle of Chernaya, and was during the bombardment during the assault on Malakhov Kurgan. Despite all the horrors of the siege, Tolstoy wrote at this time the story “Cutting Wood,” which reflected Caucasian impressions, and the first of the three “Sevastopol stories” - “Sevastopol in December 1854.” He sent this story to Sovremennik. Immediately printed, the story was read with interest throughout Russia and made a stunning impression with the picture of the horrors that befell the defenders of Sevastopol. The story was noticed by Emperor Alexander II; he ordered to take care of the gifted officer.
For the defense of Sevastopol, Tolstoy was awarded the Order of St. Anne with the inscription “For Honor,” medals “For the Defense of Sevastopol 1854-1855” and “In Memory of the War of 1853-1856.” Surrounded by the brilliance of fame, enjoying the reputation of a brave officer, Tolstoy had every chance of a career, but he ruined it for himself by writing several satirical songs, stylized as soldiers' songs. One of them is dedicated to the failure of the military operation on August 4 (16), 1855, when General Read, misunderstanding the order of the commander-in-chief, attacked the Fedyukhin Heights. The song entitled “Like the fourth, the mountains carried us hard to take away,” which affected a number of important generals, was a huge success. Leo Tolstoy answered for her to the assistant chief of staff A. A. Yakimakh. Immediately after the assault on August 27 (September 8), Tolstoy was sent by courier to St. Petersburg, where he completed “Sevastopol in May 1855.” and wrote “Sevastopol in August 1855,” published in the first issue of Sovremennik for 1856 with the author’s full signature.
“Sevastopol Stories” finally strengthened his reputation as a representative of the new literary generation, and in November 1856 the writer parted with military service forever.
Traveling around Europe
In St. Petersburg he was warmly welcomed in high society salons and literary circles; He became especially close friends with Turgenev, with whom he lived in the same apartment for some time. The latter introduced him to the Sovremennik circle, after which Tolstoy established friendly relations with Nekrasov, Goncharov, Panaev, Grigorovich, Druzhinin, Sollogub.
At this time, “Blizzard”, “Two Hussars” were written, “Sevastopol in August” and “Youth” were completed, and the writing of the future “Cossacks” continued.
The cheerful life was not slow to leave a bitter aftertaste in Tolstoy’s soul, especially since he began to have a strong discord with the circle of writers close to him. As a result, “people became disgusted with him and he became disgusted with himself” - and at the beginning of 1857, Tolstoy left St. Petersburg without any regret and went abroad.
On his first trip abroad, he visited Paris, where he was horrified by the cult (“The idolization of a villain, terrible”), at the same time he attends balls, museums, and is fascinated by the “sense of social freedom.” However, his presence at the guillotine made such a grave impression that Tolstoy left Paris and went to places associated with Rousseau - to Lake Geneva.
Lev Nikolaevich writes the story “Albert”. At the same time, his friends never cease to be amazed at his eccentricities: in his letter to I. S. Turgenev in the fall of 1857, P. V. Annenkov tells of Tolstoy’s project to plant forests throughout Russia, and in his letter to V. P. Botkin, Leo Tolstoy reports how very happy he was the fact that he did not become only a writer, contrary to Turgenev’s advice. However, in the interval between the first and second trips, the writer continued to work on “Cossacks”, wrote the story “Three Deaths” and the novel “Family Happiness”.
His last novel was published in “Russian Bulletin” by Mikhail Katkov. Tolstoy's collaboration with the Sovremennik magazine, which lasted from 1852, ended in 1859. In the same year, Tolstoy took part in organizing the Literary Fund. But his life was not limited to literary interests: on December 22, 1858, he almost died on a bear hunt. Around the same time, he began an affair with the peasant woman Aksinya, and plans for marriage were ripening.
On his next trip, he was mainly interested in public education and institutions aimed at raising the educational level of the working population. He closely studied issues of public education in Germany and France, both theoretically and practically, and through conversations with specialists. Of the outstanding people in Germany, he was most interested in Auerbach as the author of the “Black Forest Stories” dedicated to folk life and as a publisher of folk calendars. Tolstoy paid him a visit and tried to get closer to him. In addition, he also met with the German teacher Disterweg. During his stay in Brussels, Tolstoy met Proudhon and Lelewell. In London he visited Herzen and attended a lecture by Dickens.
Tolstoy’s serious mood during his second trip to the south of France was also facilitated by the fact that his beloved brother Nikolai died of tuberculosis in his arms. The death of his brother made a huge impression on Tolstoy.
The stories and essays he wrote in the late 1850s include “Lucerne” and “Three Deaths.” Gradually, criticism for 10-12 years, before the appearance of “War and Peace,” cooled towards Tolstoy, and he himself did not strive for rapprochement with writers, making an exception for Afanasy Fet.
One of the reasons for this alienation was the quarrel between Leo Tolstoy and Turgenev, which occurred while both prose writers were visiting Fet on the Stepanovo estate in May 1861. The quarrel almost ended in a duel and ruined the relationship between the writers for 17 long years.
Treatment in the Bashkir nomadic camp Karalyk
In 1862, Lev Nikolaevich was treated with kumis in the Samara province. Initially, I wanted to be treated at Postnikov’s kumiss hospital near Samara, but due to the large number of vacationers, I went to the Bashkir nomadic camp Karalyk, on the Karalyk River, 130 versts from Samara. There he lived in a Bashkir tent (yurt), ate lamb, basked in the sun, drank kumiss, tea and played checkers with the Bashkirs. The first time he stayed there for a month and a half. In 1871, Lev Nikolaevich came again due to deteriorating health. Lev Nikolaevich lived not in the village itself, but in a tent near it. He wrote: “The melancholy and indifference have passed, I feel myself returning to the Scythian state, and everything is interesting and new... Much is new and interesting: the Bashkirs, who smell of Herodotus, and Russian men, and villages, especially charming in the simplicity and kindness of the people.” . In 1871, having fallen in love with this region, he bought from Colonel N.P. Tuchkov an estate in the Buzuluk district of the Samara province, near the villages of Gavrilovka and Patrovka (now Alekseevsky district), in the amount of 2,500 acres for 20,000 rubles. Lev Nikolaevich spent the summer of 1872 on his estate. A few fathoms from the house there was a felt tent in which lived the family of the Bashkir Muhammad Shah, who made kumiss for Lev Nikolaevich and his guests. In general, Lev Nikolaevich visited Karalyk 10 times in 20 years.
Pedagogical activity
Tolstoy returned to Russia shortly after the liberation of the peasants and became a peace mediator. Unlike those who looked at the people as a younger brother who needed to be raised to their level, Tolstoy thought, on the contrary, that the people were infinitely higher than the cultural classes and that the gentlemen needed to borrow the heights of spirit from the peasants. He actively began setting up schools in his Yasnaya Polyana and throughout the Krapivensky district.
The Yasnaya Polyana school belonged to the number of original pedagogical attempts: in the era of admiration for the German pedagogical school, Tolstoy resolutely rebelled against any regulation and discipline in the school. In his opinion, everything in teaching should be individual - both the teacher and the student, and their mutual relationships. At the Yasnaya Polyana school, the children sat where they wanted, as much as they wanted, and as they wanted. There was no specific teaching program. The teacher's only job was to get the class interested. The classes went well. They were led by Tolstoy himself with the help of several regular teachers and several random ones, from his closest acquaintances and visitors.
Since 1862, he began publishing the pedagogical magazine “Yasnaya Polyana”, where he himself was the main employee. In addition to theoretical articles, Tolstoy also wrote a number of stories, fables and adaptations. Combined together, Tolstoy's pedagogical articles made up an entire volume of his collected works. At one time they went unnoticed. No one paid attention to the sociological basis of Tolstoy’s ideas about education, to the fact that Tolstoy saw only simplified and improved ways of exploiting the people by the upper classes in education, science, art and technological successes. Moreover, from Tolstoy’s attacks on European education and “progress,” many concluded that Tolstoy was a “conservative.”
Soon Tolstoy left teaching. Marriage, the birth of his own children, plans related to writing the novel “War and Peace” push back his pedagogical activities by ten years. Only in the early 1870s did he begin to create his own “ABC” and publish it in 1872, and then release the “New ABC” and a series of four “Russian books for reading”, approved as a result of long ordeals by the Ministry of Public Education as manuals for primary educational institutions. Classes at the Yasnaya Polyana school resume briefly.
It is known that the Yasnaya Polyana school had a certain influence on other domestic teachers. For example, it was S. T. Shatsky who initially took it as a model when creating his own school “Cheerful Life” in 1911.
Acting as a defense attorney in court
In July 1866, Tolstoy appeared at a military court as a defender of Vasil Shabunin, a company clerk stationed near Yasnaya Polyana of the Moscow Infantry Regiment. Shabunin hit the officer, who ordered him to be punished with canes for being drunk. Tolstoy argued that Shabunin was insane, but the court found him guilty and sentenced him to death. Shabunin was shot. This case made a great impression on Tolstoy.
From his youth, Lev Nikolaevich knew Lyubov Alexandrovna Islavina, married to Bers (1826-1886), and loved to play with her children Lisa, Sonya and Tanya. When the Bersov daughters grew up, Lev Nikolaevich thought about marrying his eldest daughter Lisa, he hesitated for a long time until he made a choice in favor of his middle daughter Sophia. Sofya Andreevna agreed when she was 18 years old, and the count was 34 years old. On September 23, 1862, Lev Nikolaevich married her, having previously admitted his premarital affairs.
For a certain period of time, the brightest period of his life begins for Tolstoy - the rapture of personal happiness, very significant thanks to the practicality of his wife, material well-being, outstanding literary creativity and, in connection with it, all-Russian and world fame. It would seem that in his wife he found an assistant in all matters, practical and literary - in the absence of a secretary, she rewrote her husband’s drafts several times. But very soon happiness is overshadowed by inevitable petty disagreements, fleeting quarrels, mutual misunderstandings, which only worsened over the years.
The wedding of Sergei Nikolaevich Tolstoy’s older brother with Sofia Andreevna’s younger sister, Tatyana Bers, was also planned. But Sergei’s unofficial marriage to a gypsy woman made the marriage of Sergei and Tatyana impossible.
In addition, Sofia Andreevna’s father, physician Andrei Gustav (Evstafievich) Bers, even before his marriage to Islavina, had a daughter, Varvara, from V.P. Turgeneva, the mother of I.S. Turgenev. On her mother’s side, Varya was the sister of I. S. Turgenev, and on her father’s side, S. A. Tolstoy, thus, together with marriage, Leo Tolstoy acquired a relationship with I. S. Turgenev.
From the marriage of Lev Nikolaevich with Sofia Andreevna, a total of 13 children were born, five of whom died in childhood. Children:
- Sergei (July 10, 1863 - December 23, 1947), composer, musicologist.
- Tatiana (October 4, 1864 - September 21, 1950). Since 1899 she has been married to Mikhail Sergeevich Sukhotin. In 1917-1923 she was the curator of the Yasnaya Polyana museum-estate. In 1925 she emigrated with her daughter. Daughter Tatyana Mikhailovna Sukhotina-Albertini (1905-1996).
- Ilya (May 22, 1866 - December 11, 1933), writer, memoirist
- Lev (1869-1945), writer, sculptor.
- Maria (1871-1906) Buried in the village. Kochaki of Krapivensky district (modern Tula region, Shchekinsky district, village of Kochaki). Since 1897 she has been married to Nikolai Leonidovich Obolensky (1872-1934).
- Peter (1872-1873).
- Nikolai (1874-1875).
- Varvara (1875-1875).
- Andrey (1877-1916), official for special assignments under the Tula governor. Participant in the Russian-Japanese War.
- Mikhail (1879-1944).
- Alexey (1881-1886).
- Alexandra (1884-1979).
- Ivan (1888-1895).
As of 2010, there were a total of more than 350 descendants of Leo Tolstoy (including both living and deceased), living in 25 countries around the world. Most of them are descendants of Lev Lvovich Tolstoy, who had 10 children, the third son of Lev Nikolaevich. Since 2000, once every two years, meetings of the writer’s descendants have been held in Yasnaya Polyana.
Creativity flourishes
During the first 12 years after his marriage, he created War and Peace and Anna Karenina. At the turn of this second era of Tolstoy’s literary life stand the works conceived back in 1852 and completed in 1861-1862. “Cossacks” is the first of the works in which Tolstoy’s talent was most realized.
"War and Peace"
Unprecedented success befell War and Peace. An excerpt from the novel entitled "1805" appeared in the Russian Messenger of 1865; in 1868 three of its parts were published, soon followed by the remaining two. The release of War and Peace was preceded by the novel The Decembrists (1860-1861), to which the author returned several times, but which remained unfinished.
In Tolstoy's novel all classes of society are represented, from emperors and kings to the last soldier, all ages and all temperaments throughout the entire reign of Alexander I.
"Anna Karenina"
The endlessly happy rapture of the bliss of existence is no longer present in Anna Karenina, dating back to 1873-1876. There is still a lot of joyful experience in the almost autobiographical novel of Levin and Kitty, but there is already so much bitterness in the depiction of Dolly’s family life, in the unhappy ending of the love of Anna Karenina and Vronsky, so much anxiety in Levin’s mental life that in general this novel is already a transition to the third period Tolstoy's literary activity.
In January 1871, Tolstoy sent a letter to A. A. Fet: “ How happy I am... that I will never write verbose rubbish like “War” again» .
On December 6, 1908, Tolstoy wrote in his diary: “ People love me for those trifles - “War and Peace”, etc., which seem very important to them»
In the summer of 1909, one of the visitors to Yasnaya Polyana expressed his delight and gratitude for the creation of War and Peace and Anna Karenina. Tolstoy replied: “ It’s the same as if someone came to Edison and said: “I really respect you because you dance the mazurka well.” I attribute meaning to completely different books of mine (religious!)».
In the sphere of material interests, he began to say to himself: “ Well, okay, you will have 6,000 acres in the Samara province - 300 heads of horses, and then?"; in the literary field: " Well, okay, you will be more famous than Gogol, Pushkin, Shakespeare, Moliere, all the writers in the world - so what!" As he began to think about raising children, he asked himself: “ For what?"; discussing “how the people can achieve prosperity,” he “ suddenly he said to himself: what does it matter to me?"In general, he " felt that what he stood on had given way, that what he had lived on was no longer there.” The natural result was thoughts of suicide.
« I, a happy man, hid the cord from myself so as not to hang myself on the crossbar between the closets in my room, where I was alone every day, undressing, and stopped going hunting with a gun so as not to be tempted by too easy a way to rid myself of life. I myself didn’t know what I wanted: I was afraid of life, I wanted to get away from it and, meanwhile, I hoped for something else from it.».
Other works
In March 1879, in the city of Moscow, Leo Tolstoy met Vasily Petrovich Shchegolenok and in the same year, at his invitation, he came to Yasnaya Polyana, where he stayed for about a month and a half. The Goldfinch told Tolstoy many folk tales and epics, of which more than twenty were written down by Tolstoy, and Tolstoy, if he didn’t write them down on paper, remembered the plots of some (these notes are published in Volume XLVIII of the Anniversary Edition of Tolstoy’s Works). Six works written by Tolstoy are sourced from legends and stories of Shchegolenok (1881 - “How People Live”, 1885 - “Two Old Men” and “Three Elders”, 1905 - “Korney Vasiliev” and “Prayer”, 1907 - “Old Man in the Church”) . In addition, Count Tolstoy diligently wrote down many sayings, proverbs, individual expressions and words told by the Goldfinch.
Last journey, death and funeral
On the night of October 28 (November 10), 1910, L.N. Tolstoy, fulfilling his decision to live his last years in accordance with his views, secretly left Yasnaya Polyana, accompanied by his doctor D.P. Makovitsky. He began his last journey at Shchekino station. On the same day, having transferred to another train at the Gorbachevo station, he reached the Kozelsk station, hired a coachman and headed to Optina Pustyn, and from there the next day to the Shamordino Monastery, where Tolstoy met his sister, Maria Nikolaevna Tolstoy. Later, Tolstoy’s daughter, Alexandra Lvovna, came to Shamordino with her friend.
On the morning of October 31 (November 13) L.N. Tolstoy and his entourage went from Shamordino to Kozelsk, where they boarded train No. 12, which had already arrived at the station, heading south. There was no time to buy tickets upon boarding; Having reached Belyov, we purchased tickets to Volovo station. According to the testimony of those accompanying Tolstoy, the trip had no specific purpose. After the meeting, we decided to go to Novocherkassk, where we would try to get foreign passports and then go to Bulgaria; if this fails, go to the Caucasus. However, on the way, L.N. Tolstoy fell ill with pneumonia and was forced to get off the train that same day at the first large station near the settlement. This station turned out to be Astapovo (now Leo Tolstoy, Lipetsk region), where on November 7 (20) L. N. Tolstoy died in the house of the station chief I. I. Ozolin.
On November 10 (23), 1910, he was buried in Yasnaya Polyana, on the edge of a ravine in the forest, where as a child he and his brother were looking for a “green stick” that held the “secret” of how to make all people happy.
In January 1913, a letter from Countess Sophia Tolstoy dated December 22, 1912 was published, in which she confirms the news in the press that his funeral service was performed at the grave of her husband by a certain priest (she refutes rumors that he was not real) in her presence. In particular, the countess wrote: “I also declare that Lev Nikolaevich never once before his death expressed a desire not to be buried, and earlier he wrote in his diary in 1895, as if a will: “If possible, then (bury) without priests and funeral services. But if this will be unpleasant for those who will bury, then let them bury as usual, but as cheaply and simply as possible."
Report of the head of the St. Petersburg security department, Colonel von Kotten, to the Minister of Internal Affairs of the Russian Empire:
« In addition to the reports of November 8th, I am reporting to Your Excellency information about the unrest of student youth that took place on November 9th... on the occasion of the burial day of the deceased L.N. Tolstoy. At 12 noon, a memorial service for the late L.N. Tolstoy was celebrated in the Armenian Church, which was attended by about 200 people praying, mostly Armenians, and a small part of students. At the end of the funeral service, the worshipers dispersed, but a few minutes later students and female students began to arrive at the church. It turned out that announcements were posted on the entrance doors of the university and the Higher Women's Courses that a memorial service for L.N. Tolstoy would take place on November 9 at one o'clock in the afternoon in the above-mentioned church. The Armenian clergy performed a requiem service for the second time, by the end of which the church could no longer accommodate all the worshipers, a significant part of whom stood on the porch and in the courtyard of the Armenian Church. At the end of the funeral service, everyone on the porch and in the church yard sang “Eternal Memory”...»
There is also an unofficial version of the death of Leo Tolstoy, stated in emigration by I.K. Sursky from the words of a Russian police official. According to it, the writer, before his death, wanted to reconcile with the church and came to Optina Pustyn for this. Here he awaited the order of the Synod, but, feeling unwell, was taken away by his arriving daughter and died at the Astapovo post station.