We read syllables with m. We learn to read by syllables in a playful way
Trainer for beginners. Simple words.
The book is wonderful. But kids don’t want to strain themselves and put the letters into words; it’s much easier to look at the picture and guess from the very first letter what is written under the picture.
Therefore, I suggest downloading these sheets. They have a lot of words and no explanatory pictures. Nothing will distract your child from the reading process. And since each word has only three letters, reading them will not be very difficult.
How many of them are words consisting of three letters? There are more than a hundred such words on these leaves. So the child will have something to read.

New cards for practicing reading skills. This time the selection contains words of 4 letters, but with one syllable.
That is, words have only one vowel letter.
DAY, LOAD, DEADLINE, OVEN, SEVEN, NIGHT and so on.
More than 100 words consisting of 4 letters and 1 syllable are collected on two sheets.
When reading, a child must not only form a word from letters, but also comprehend what he read. Ask your child to explain each new word.


We continue to practice our reading skills.
The next selection is already two-syllable words of 4 letters. On the first card are words with the so-called “open syllable”. They are easy to read. Ma-ma, ka-sha, ne-bo, re-ka, lu-zha and similar words.
The second card is more difficult. The words on it contain both open and closed syllables. Ma-yak, ig-la, u-tyug, yah-ta, o-sel, yol-ka and so on.
Each card has over fifty words. So the child will have to work hard until he reads all the words.


We read new words syllable by syllable. Words already consist of 5 letters. Va-gon, baby, tu-man, mar-ka, re-dis, lamp-pa. And so on. If your child confidently reads these hundred and fifty words, you can assume that your baby HAS LEARNED how to read! Or rather, he learned to put words together from letters.
Download another reading simulator. The first letter is M. All tasks are the same as for the previous letters. First, practice reading the merge syllable. Then move on to reading words syllable by syllable. And at the end there are some suggestions for reading.
Download another reading simulator.
The first letter is M.
All tasks are the same as for the previous letters.
First, practice reading fusion syllables (ma-mo-mu-we-mi-me-me-me-myo-mu).
Then move on to reading words syllable by syllable. And at the end, as always, a few sentences for reading.


Dear readers!
All materials from the site can be downloaded absolutely free. All files have been scanned by antivirus and do not contain hidden scripts.
Pictures in archives are not marked with watermarks.
The site is updated with materials based on the free work of the authors. If you want to thank them for their work and support our project, you can transfer any amount that is not burdensome to you to the site’s account.
Thank you in advance!!!
A child who has learned to put sounds into syllables, syllables into words, and words into sentences needs to improve their reading skills through systematic training. But reading is a rather labor-intensive and monotonous activity, and many children lose interest in it. Therefore we offer small texts, the words in them are divided into syllables.
At first read the work to your child yourself, and if it is long, you can read its beginning. This will interest the child. Then invite him to read the text. After each work, questions are given to help the child better understand what he read and comprehend the basic information that he gleaned from the text. After discussing the text, suggest reading it again.
Smart Bo-bik
So-nya and so-ba-ka Bo-bik go-la-li.
So-nya played with the doll.
Then So-nya ran home and forgot the doll.
Bo-bik found the doll and brought it to So-na.
B. Korsunskaya
Answer the questions.
1. Who did Sonya walk with?
2. Where did Sonya leave the doll?
3. Who brought the doll home?
The bird made a nest on a bush. The children found a nest and took it down to the ground.
- Look, Vasya, three birds!
The next morning the children arrived, but the nest was already empty. It would be a pity.
L. Tolstoy
Answer the questions.
1. What did the children do with the nest?
2. Why was the nest empty the next morning?
3. Did the children do well? What would you do?
4. Do you think this work is a fairy tale, story or poem?
Peti and Misha had a horse. They began to argue: whose horse is it? Did they start tearing horses from each other?
- Give me my horse.
- No, give it to me - the horse is not yours, but mine.
The mother came, took the horse, and the horse became no one’s.
L. Tolstoy
Answer the questions.
1. Why did Petya and Misha quarrel?
2. What did mom do?
3. Did the children play horse well? Why are you so
do you think?

It is advisable to use the example of these works to show children the genre features of poems, stories and fairy tales.
A genre of oral fiction that contains unusual events in everyday life (fantastic, miraculous or everyday) and is distinguished by a special compositional and stylistic structure. Fairy tales contain fairy-tale characters, talking animals, and unprecedented miracles occur.
Poem- a short poetic work in verse. The poems read smoothly and musically, they have rhythm, meter and rhyme.
Story- small literary form; a short narrative work with a small number of characters and the short duration of the events depicted. The story describes an incident from life, some striking event that really happened or could happen.
In order not to discourage him from reading, do not force him to read texts that are uninteresting and inaccessible to his understanding. It happens that a child takes a book he knows and reads it “by heart.” Necessarily read to your child every day poems, fairy tales, stories.
Daily reading enhances emotionality, develops culture, horizons and intellect, and helps to understand human experience.
Literature:
Koldina D.N. I read on my own. - M.: TC Sfera, 2011. - 32 p. (Sweetie).
Before learning to read, a child must learn the very concept of syllables. Before learning to read and write, your child must recognize letters and be able to relate them to sounds. The next stage is learning syllables. Interesting manuals for studying syllables can be downloaded from our website.
Is it difficult to teach a child to combine letters into syllables?How to learn to read?
At the beginning of learning to read, it is necessary to convey to the child such concepts as vowel and consonant sounds and letters. Vowel sounds can be stressed or unstressed. Among the consonants, there are voiced and voiceless, hard and soft.
By the way, special attention should be paid to the hardness and softness of sounds. This characteristic of sounds within a syllable is determined by soft or hard signs or vowels located after consonants.
So, the letters E, E, I, Yu, I indicate the softness of the previous consonant sound, and the letters E, O, U, Y indicate hardness.
A table of all syllables on our website will help illustrate soft and hard consonant sounds. It can be read online or downloaded and printed from our website.
Syllables for children to learn to read can be presented in the form of a game. To teach your child to read, you need to download a table of syllables and print it. Then cut into individual cards. To prevent syllables and cards from becoming wrinkled, they can be glued onto thick cardboard. Now we will try to introduce syllable combinations to children in the form of a game.
Games for learning to read
A table of all syllables, which you will need to download from our website, will help you teach your child to read. Soft and hard consonants, as well as vowel sounds and letters are indicated in different colors for contrast. Thus, syllable combinations look bright and colorful.
First, we teach the child to distinguish syllables in Russian from each other. To do this, you will need not only cards where the syllables of the language to be read are written, but also a whole table of syllables. To do this, you will have to download and print it again. We lay out the table and ask the child to match the cards with syllables and the corresponding cell in the table. So gradually the baby will remember individual syllable combinations and name them, and then read them. Thus, we form a lotto from a table, only instead of images there are letter combinations.
At the next stage of learning to read, we offer the child a couple of different syllables and combine them into a word. Please note that before starting this game, the child must read individual syllable combinations well and then put them into words. For example, we take the syllable ZHA and add the syllable BA to it. It turns out to be a TOAD. You can draw arrows or come up with a fairy-tale character who will walk from one syllable to another and connect them into words. As a result of such a simple game, the child will quickly learn to read.
Syllable tables
Since letter combinations are represented in large numbers in the Russian language, we suggest studying each consonant separately in combination with all vowels. Thus, the table for one game becomes much smaller in volume, and it is easier for the child to put all the syllables in their places. You can also download these tables on our website. Here are examples of what syllables might look like for your kids in tables:
Common mistakes
Often in speech, children confuse syllables with the letters “x”, “g” and syllables with the letters “g”, “k”. Confusion also occurs when a child pronounces syllables with the letter “d”, “g” or syllables with the letter “k”, “p”. These consonants sound very similar. When making words from them, try to pronounce them as clearly as possible. At the stage of learning to read, you can download tables with similar sounds, cut cards from them and try to create words that sound similar, focusing on the difference in spelling.
When studying Russian letter combinations with children, try to interest them. If you have a magnetic alphabet at home, try to form some words from the letters. They can be conveniently attached to your tablet and then read. Let the child make up his own word combinations and you read them.
Word creation should be a group game: one child will not be interested. Teach your baby and learn with him!
Teaching a child to read. We remember the syllables. Learning to read a syllable. Merging letters into syllables. Syllable fusion. How to teach a child to read syllables. Transition from letter to syllable.
Currently, the market for children's educational literature is filled with a variety of alphabet books and primers for preschoolers. Unfortunately, many authors do not provide guidelines on how to teach reading. The first pages of the manuals introduce children to some letters, then parents are invited to complete tasks together with their children such as “add syllables with the letter A and read them”, “compose, write and read syllables”, and sometimes they do not have such explanations, but simply on the pages syllables appear for reading. But how can a child read a syllable?
Thus, N.S. Zhukova in her “Primer” illustrates the fusion of consonant and vowel with the help of a “running man.” He suggests showing the first letter with a pencil (pointer), moving the pencil (pointer) to the second letter, connecting them with a “path,” while pulling the first letter until “you and the little man run along the path to the second letter.” The second letter must be read so that “the track does not break.”
We find another way to facilitate syllable fusion in the book by Yu. V. Tumalanova “Teaching Children 5-6 Years Old to Read.” The methodological part of the book offers different options for accompanying syllable fusion:
The adult holds one letter in his hands, the child reads, at the same time another letter is brought from afar, and the first one “falls”, the child proceeds to read a new letter,
An adult holds letters in his hands, one high, the other lower, the child begins to read the upper letter, slowly approaching the lower one, and proceeds to read the lower one,
The adult holds a card in his hands with letters written on both sides, the child reads the letter on one side, the adult turns the card over to the other side, the child continues to read.
On the pages intended for working with children, we see the following original images of syllables:

The techniques outlined above relate to the sound analytical-synthetic method of teaching reading. “The letter I after a consonant denotes its softness, which means that in the combination VI the letter B denotes a soft sound. It turns out VI.” This is roughly what the chain of inference looks like when reading a syllable through sound-letter analysis. And what will be the chain when reading, for example, the words CROCODILES? Can a child easily learn to read in this “long” way? Yes, there are children even of primary preschool age who, thanks to the high organization of analytical-synthetic thinking, are able to successfully master reading in this way. But for most children this method is too difficult. It does not correspond to the age-related organization of cognitive activity. Even when using the auxiliary techniques outlined above, children still cannot master reading using the sound analytical-synthetic method, or the formation of reading skills is difficult, interest in classes is lost, psychological problems develop (low self-esteem, protest reactions, slow development of cognitive processes characteristic of a given age).
Try to read any sentence and at the same time observe how words are formed from letters. You simply reproduce different types of syllables from memory and comprehend their combinations! It is recollection that helps us read quickly, bypassing the stage of constructing chains of inferences about the sound-letter composition of a word.
Based on this, we can understand that it is easier for a child to learn to read by memorizing a system of reading units - fusion syllables. This method of teaching reading will be most successful for children of older preschool age. It is at this age that memory, all its types (auditory, visual, “movement” memory, combined, semantic, etc.) and processes (memorization, storage and reproduction of information) most actively develop and improve.
You need to memorize syllables according to the same scheme that is used when memorizing letters:
Repeated naming of a syllable by an adult;
- search for a syllable according to the instructions of an adult, followed by naming;
- independent naming - “reading” a syllable.
Of course, the child should be interested in studying. When introducing a child to syllables, you can use short fairy tales composed according to the same principle: a consonant letter, traveling, meets vowel letters on its way, all in turn, and in pairs they sing “songs” - syllables. A consonant letter can “go to the forest to pick mushrooms”, can “ride the elevator”, can “visit girlfriends - vowel letters” and much more that your imagination is capable of. You can make large letters cut out of colored cardboard with faces and handles, then the vowel and consonant letters also “take hands and sing a song together” (syllable). Don't think that you have to make up such tales for each consonant letter. The child will soon be able to tell tales about syllables himself, and will be able to name even new syllables by analogy with those he has already mastered reading.

The order in which you introduce the syllables is not important; it will be determined by the alphabet that you choose to teach your child to read. Some alphabets set the sequence of learning according to the frequency of use of letters in the language, others in accordance with the sequence of formation of sounds in children, others - according to the intention of the authors of the manuals.
After the child’s initial familiarization with syllables that can be formed using a consonant, it is necessary to create situations where the child will look for the syllable given by the adult. Write the syllables on separate pieces of paper and place them in front of the child:
Ask to bring a “brick” of KA, or KO, or CU, etc. on a truck;
- “turn” leaves with syllables into candies, treat the doll with “candy” KI, or KE, or KO, etc.;
Play “postman” - deliver “letters”-syllables to members of your family, for example: “Take it to grandma KU”, “Take a letter to PE for dad”, etc.;
Lay out the syllables on the floor, “turn” the child into an airplane, and command which airfield to land on.
You can also search for a given syllable on the pages of the alphabet or primer. In this case, the game situation may look like teaching your favorite toy to read (“Show Pinocchio the syllable PU!”, and immediately after the show - “Tell him what syllable it is”).
You can cut the syllables written on pieces of paper horizontally or diagonally (but not vertically, otherwise the syllable will be divided into letters). You give the child the top part of a syllable, name the syllable, ask him to find the bottom part, then make up the halves and name the syllable.
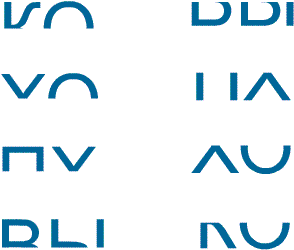
If the child confidently holds a pencil in his hand and knows how to write or trace letters, write with a dotted line the syllables that you are learning with the child, offer to trace the syllable you named, you can trace different syllables with pencils of different colors.
Always after completing tasks to find a syllable, ask the child what syllable it is (but not “Read what is written!”). In these learning situations, the child only needs to remember the task with which syllable he completed; you yourself named this syllable when you gave the task. If the child cannot remember a syllable, offer him a choice of several answer options: “Is this GO or GU?”, “LE? BE? SE?”. This way you will protect the child from forced letter-by-letter analysis of a syllable ("G and O, will... Will... Will..."), which will cause negative emotions in him, as it will complicate the reading process. Children who get used to “seeing” individual letters in a syllable and trying to “put them together” often for a long time cannot move on to syllabic reading and reading whole words; “putting together” words from letters does not give them the opportunity to increase their reading speed.
Is it worth learning all the syllables with equal persistence? No! Pay attention to syllables that are rarely found in the Russian language (usually with the vowels Yu, Ya, E); do not insist on confident reading of these syllables if the child has difficulty remembering them. The words RYUSHA, RYASA, NETSKE and the like are not so often found in books!
A unique screen for success in teaching a child to read can be the Syllable House, which the child himself will “build” as he learns fusion syllables. To make it you will need a large sheet of paper (whatman paper, wallpaper), felt-tip pens or paints, glue and colored paper or cardboard. On a large sheet of paper you need to draw the “frame” of the house: write the vowels below horizontally (you can depict them in arched entrances), write the consonants vertically from bottom to top in the order suggested by your alphabet or primer (it will be more interesting if the consonants the letters will “stand on balconies”). The frame is ready. Now, on separate pieces of paper - “bricks” - write the syllables you are currently studying. Ask your child to find the syllables according to your assignment, determine the place of this “brick” in the house (horizontally - “floor”, vertically - “entrance”), glue the syllable in its place. Now, after practicing with a group of syllables, you can paste them into this house. This way the house will grow floor by floor, and the child will see his progress in mastering reading.
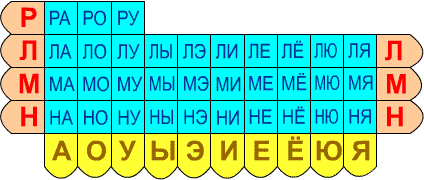
In fact, the Syllable House is an analogue of a table for reading according to Zaitsev’s method. But in this option, only those syllables that he has already begun to master will appear before the child’s eyes, and you determine the order of the syllables yourself (at your discretion or according to the order in which the letters appear in the alphabet).
Working with the table does not end there. The following exercises are carried out according to the table:
Search for a syllable according to instructions (adult names, child finds, shows, names);
Reading chains of syllables - by vowel (MA - NA - RA - LA - PA -...), by consonant (PA-PO-PU-PY-...);
Reading syllables with completion of the word (KA - porridge, KU - chicken,...);
In the future, using the table, you can guess words for the child, showing them syllable by syllable, or the child, according to his own plan or the instructions of an adult, will be able to compose words himself. In such a table, the child will see the absence of some “bricks” - ZHY, SHY, CHYA, SHCHYA, CHYU, SHCHYU. Perhaps this will be the first step in mastering Russian spelling.
Quite rarely, but such tasks are still found in notebook books. The child needs to color a picture divided into parts. Each part is signed with a syllable. Each syllable is painted with its own color.
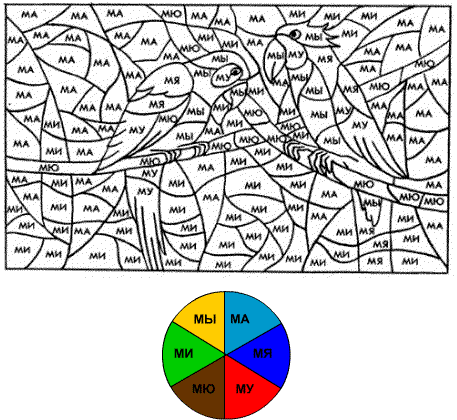
When performing such a task, a natural possibility arises of repeatedly naming a syllable, and therefore memorizing it. Work on the task sequentially: first one syllable, then another... First, show and name the syllable yourself, determine the color to paint it, then, when the child finds and paints the corresponding detail of the picture, ask what syllable is written here.
Syllable + picture
At the stage of independent reading, the exercise “Syllable + picture” is used. These kinds of tasks are rarely found in textbooks, but they are very useful, as they contribute to the early formation of meaningful reading.
The child is asked to connect the picture with the syllable with which its name begins.
ATTENTION! We draw your attention to the fact that in this and subsequent exercises, words must be selected in which the pronunciation of the 1st syllable coincides with its spelling (for example, the word “vata” is suitable, but “water” is not, because it is pronounced “vada” ").
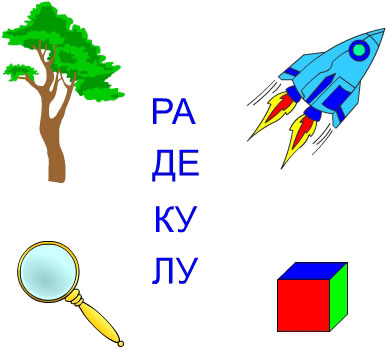
In another version of the task, different syllables are labeled under each picture; the child needs to choose the correct first syllable of the name of the object shown in the picture.

You can create such tasks yourself: use the syllables you have previously written and match them with corresponding pictures from any board game or lotto.
The most difficult ones when teaching preschoolers to read are the merging syllables, which we talked about above, but in the Russian language, in addition to merging syllables, there are other types of syllables - a reverse syllable (AM, AN...), a closed syllable (SON, CON...). .), a syllable with a combination of consonants (SLO, SKO...). Each of these types of syllables requires special attention when learning; training in naming and reading them is necessary to simplify the further transition to reading with words.
Thus, it is necessary to prevent the incorrect reading of a reverse syllable: they consist, like a merger, of a consonant and a vowel, and a preschooler can read a reverse syllable as a merger by rearranging the letters when reading (TU instead of UT). It will be useful to compare and read pairs of syllables - merged and open, consisting of the same letters (MA - AM, MU - UM, MI - IM, etc.).
When learning to read a closed syllable, invite your child to read pairs and chains of such syllables that are similar in the merger they contain (VAM - VAS - VAK - VAR - VAN, etc.) or in the “read” consonant (VAS - MAC - PAS, MOS - ICC, etc.). Similar work must be carried out when learning to read syllables with consonant clusters (SKA - SKO - SMU - SPO, SKA - MKA - RKA - VKA - LKA, etc.) Exercises of this content, which are presented in the textbook you have chosen, may be It’s not enough, you can create such chains yourself. Sometimes children do not like this type of work because of some of its monotony; in this case, offer not only to read the syllable, but also to finish it to the word (SKO - soon, MOS - bridge...). This exercise is not only fun, but also develops the child’s phonemic awareness, and will also contribute to meaningful reading of words in the future.
So, when learning to read a syllable, remember!
A feature of preschool children is their physiological unpreparedness to learn the rules of syllable fusion and their use in reading.
Before the child himself can name a merging syllable, he needs to hear its name many times and practice finding the syllable according to your instructions.
If a child has difficulty naming a syllable, offer him several answer options to help, thereby preventing him from switching to letter-by-letter reading of the syllable.
The most difficult to remember are the first groups of memorized syllables; then, by analogy, the child begins to name syllables that are similar in vowel or consonant.
The pace of mastering syllables should correspond to the child’s capabilities. It is better to master a smaller number of consonants and corresponding syllables, but to automatically recognize and read the syllables.
The skill of reading syllables of different types contributes to the fastest learning of a child to read whole words.
You will find an online primer (alphabet), games with letters, games for learning to read syllables, games with words and whole sentences, texts for reading. Bright, colorful pictures and a playful way of presenting the material will make reading lessons for preschoolers not only useful, but also interesting.