Forms of the words to be. How to use the verb to be correctly in English
Your application is accepted
Our manager will contact you soon
Close
There was an error sending
Send again
One of the first questions that students ask their English teacher in class: What is verb to be and why is it needed?
The verb to be is one of the most frequently used verbs, as it can act as a semantic, auxiliary, modal and connective verb. The meaning of the verb to be is "to be, to be". Unlike other English verbs, the verb to be is conjugated (that is, it changes in person and number).
Conjugation of the verb to be in the Present Simple
Today we will talk about the verb to be in the Present Indefinite tense as a semantic or independent verb, which acts as a linking verb in a sentence. Unlike the Russian language, in English the linking verb is never omitted, since the English sentence has a strictly fixed word order: subject ( subject) + predicate ( verb) + addition ( object).
Verb to be does not change according to the rules, its forms must be remembered. In the Present Indefinite tense, the verb tobe varies depending on the number and person in which the subject appears, and has three main forms am, is, are.
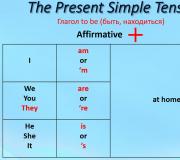
Affirmative sentences with the verb to be
I am happy I (am) happy You are happy You (are) happy He is happy He (is) happy She is happy She (is) happy It is happy It (is) happy We are happy We (are) happy You are happy You (are) happy They are happy They (are) happy

Examples of affirmative sentences with the verb to be in the Present Indefinite tense:
I am in the room. I'm in the room. The book is on the table. The book is on the table. I am a doctor. I am a doctor. (I am a doctor.)
Negative sentences with the verb to be in the Present Indefinite tense:
I am not happy I am not happy You are not happy You are not happy He is happy He is not happy She is not happy She is not happy It is not happy It is not )happy We are not happy We are not (are) happy You are not happy You are not (are) happy They are not happy They are not (are) happy

Examples of negative sentences with the verb to be in the Present Indefinite tense:
I am not a doctor. I am not a doctor. The weather is not bad. The weather is not bad. They are not from Paris. They are not from Paris.
Interrogative sentences with the verb to be in the Present Indefinite tense:
To form interrogative sentences with verb to be it is enough to swap the subject and predicate, that is, the personal form of the verb to be will appear before the subject
Am I happy Am I (am) happy? Are you happy? Are you (are) happy? Is he happy? Is he (is) happy? Is she happy? Is she (is) happy? Is it happy? Is it (is) happy? Are we happy? Are we (are) happy? Are you happy? Are you (are) happy? Are they happy? Are they (are) happy?

Examples of interrogative sentences with the verb to be in the Present Indefinite tense:
Is the book on the table? The book is on the table? Is the weather bad? The weather is bad? Is the book interesting? The book is interesting?
Set phrases with the verb to be
In a word, the functions of the verb as a linking verb in the Present Simple are varied. With its help, we can introduce and characterize a person, talk about the profession and our feelings, inform about the weather and location, etc. In addition, there are a huge number of common phrases that are used with the verb to be
Examples of sentences with expressions that are used with the verb to be
I am sorry. It's my fault. He is late for the meeting. Are you ready for the test? Are you ready for the test?
Often the verb to be is used in impersonal sentences, such as:
It is expensive. It's expensive It is cold. Cold. It is important to learn a foreign language. Learning a foreign language is important.
|
|
|
The English language has a fixed word order, the observance of which in Russian is not necessary: subject (subject) - predicate (predicate/verb) - object (object). In Russian, we can change words and we don’t need linking verbs.
For example, you can say: “She is happy” or “She is happy.”
You can't do this in English. The sentence must contain all the main members of the sentence (subject, verb, object) and in a certain order. Therefore, if there are no other semantic verbs, the linking verb to be is used.
Unlike other English verbs, the verb to be is conjugated (i.e., it changes in person and number)
Present form
Past tense form
Shortened forms of the verb to be:
I am = I'm
He is = He's
They are = They're
He is not = He isn’t
We are not = We aren’t
Use of the verb “to be”/Use
(where to use?)
1. full semantic verb “to be, to exist, to be”
I think, therefore I am. “I think, therefore I exist.”
2. acts as a linking verb (i.e. connects the subject with other members of the sentence)
She is happy. - She is happy.
We are from Japan. — We are from Japan.
3. as an auxiliary verb in
I' m writing an e-mail. — I'm writing an email.
She is cooking dinner. — She is preparing dinner.

If you know how to use the verb to be in English, then you can get by with just a few verbs. Without this part of speech, you will not be able to speak English at all.
Learning the verb to be is not at all difficult. You just need to learn a few forms. It's worth it! Native speakers use it much more than any other verb.
Now you will go to explore a lot of new and interesting things. You will learn what the verb to be is, how to be conjugated, get acquainted with easy tables and take a short test at the end.
What is the verb to be in English
The verb to be is found in many languages. In German - sein, in Italian - essere, in English - to be. Verb to be is an important verb in the English language.
It means ' to be, is, be’.
To help you understand, let's look at a small example:
- In Russian we say: - My name is Jessica.
— In English: — I am Jessica.
That is literally ‘I am Jessica’. If you remove am, then it will turn out to be ‘I Jessica’. Just listen to how ugly it sounds. We can say that The Verb to be adds color to English speech. Remember that the linking verb to be is never omitted. Also, the verb to be is conjugated in persons and numbers.
Conjugation of the verb to be in the present tense
You should know these forms of the verb to be in the present tense like the back of your hand. Remember and don't forget the following three forms.
The verb to be in Present Simple:
Am– for the first person singular, that is, for the pronoun I – I.
Is– for the third person singular. For pronouns – He – he, She – she, it – it.
Are– for all plural persons. For the pronoun – We – we, They – they, You – you, you.
You will need the conjugation rule throughout your English-Russian life.
Sentence forms of the verb to be in English
As you already know, the verb “to be” is conjugated by persons and numbers. This is the most basic rule that needs to be learned well at the first stage. Below you will find all the rules for constructing sentences in different forms, which are all known to you. Affirmative, negative and interrogative forms.
The conjugation tables for the verb to be in English are simple and neat, easy to remember and understand. Each pronoun has examples that will show you how the verb to be is conjugated.
Affirmative form of the verb to be
In affirmative sentences, the Subject comes first, followed by the verb “to be” and the rest of the sentence. A table of affirmative sentences will help you study this rule.
| Subject Subject |
The verb To be (to be) |
Example Example |
| I - I | am | I am crazy - I'm crazy. |
| He/she/it – he, she, it | is | She is tall - She is tall. He is a schoolboy - He is a schoolboy. It is big – It's big. |
| You/We/They – You/you, we, they | are | You are American - You are American. We are intelligent - We are smart. They are married - They are married. |
Negative form of the verb to be
In negatives, the construction remains the same, only after the verb “to be” the negative particle not appears. The negative form of the verb to be looks like this: Subject + the verb to be + not + the rest of sentence.
| Subject Subject |
The verb To be (to be) |
Example Example |
| I - I | am not | I am not from Africa - I'm not from Africa. |
| He/she/it - he, she, it | is not | She is not forty years old - She is not 40 years old. He is not a driver - He is not a driver. It is not small - It is not small. |
| You/We/They - You/you, we, they | are not | You are not American - You are not American. We are not teachers - We are not teachers. They are not stupid - They are not stupid. |
Interrogative form of the verb to be
In questions, we need to put to be in first place, and in second place the appropriate subject and the rest of the sentence. The interrogative form of the verb to be is represented by the following formula: The verb to be + subject + the rest of sentence.
| The verb To be (to be) |
Subject Subject |
Example Example |
| Am | I | Am Am I crazy? - Am I crazy? |
| Is | he/she/it | Is is she beautiful? - She's beautiful? Is he a driver? - He is a driver? Is is it here? - Is it here? |
| Are | you/we/they | Are are you slim? -Are you slim? Are are we ready? - We are ready? Are are they married? - They are married? |
When we use the verb to be we need to be careful
It is not always the case that there are only pronouns by which we can recognize which of the three forms we need to put am, is, are. Therefore, your next task will be to read sentences with the verb to be examples:
- 1. I am so happy to see you again – I’m so glad to see you again.
- 2. He is not tall enough – He is not tall enough.
- 3. The bike and the ball are in the garden – The bicycle and the ball are in the garden.
In this example, we don't have pronouns to guide us by. But there are nouns ‘bike, ball’ which can be counted 1+1=2. It follows that it is plural, so the verb to be is in the plural ‘are’. - 4. My uncle is postgraduate - My uncle is a graduate student.
There are also no pronouns in this sentence, but we know that uncle is the third person singular, that is, ‘He is a graduate student,’ which means the verb ‘to be’ is conjugated in ‘is’. - 5. My dog is disappointed because I am too busy to play with him – My dog is upset because I am too busy to play with him.
- 6. Are are you ready for lunch? -Are you ready for lunch?
- 7. We are not twins - We are not twins.

Shortened forms of the verb to be
The short form of the verb to be in present simple is constantly used both in spoken and written speech. Abbreviated forms will make it possible to understand the interlocutor. Let's look at when you can and cannot shorten the verb to be.
I am = I'm; - I am not = I’m not. (There is no short form amn't)
You are = you're; - you are not = you’re not OR you aren’t
He is = he's; - he is not = he’s not OR he isn’t (the same for the pronouns she, it)
We are = We're; - we are not = we’re not OR we aren’t
They are = they're; - they are not = they’re not OR they aren’t
Short answers with the verb To Be – Short answers
The verb To Be in the passive voice
The verb to be is also used as an auxiliary verb to form the passive form. In this case, the auxiliary verb be is followed by a verb in the past participle - the past participle. Let's look at the table, which shows the verb 'to be' in the passive voice in different tenses.
| Sample verb “Tell” - “to tell” | Present simple passive | Future passive | Preterit/Past passive | Present perfect passive | Past perfect passive |
| 1st sing – 1st person singular | I am told | I will be told | I was told | I have been told | I had been told |
| 3rd sing – 3rd person singular | It...is told | He / she ... will be told | He/she…was told | He/she…has been told | He/she…had been told |
| Etc. - and so on |
Let's look at one example:
Active voice: I eat an ice-cream - I eat ice cream.
Passive voice: The ice-cream is eaten – The ice cream has been eaten.
‘Is’ is an auxiliary verb.
The word 'Eaten' is a semantic verb that is in the Past Participle or third form.
More examples:
— We drive to work every morning - We go to work every morning. -> We are driven to work every morning – Every morning we are taken to work.
You have already learned a lot, so we suggest you relax and watch a video to reinforce the material you have learned.
Perfect form of the verb to be
The perfect form of the verb “to be” is ‘been’. The verb to be is, therefore, changes tenses.
Examples:
- They have been there before - They were there before. -> This sentence is in Present Perfect Tense. Study the table carefully and pay attention to the highlighted words. You can also download this table. Try to find the button =)
| Time | Question | Statement | Negation |
| Future Future |
I He Will She be here? It You We They |
I He She will be here. It You We They |
I He She will not be/ won’t be here. It You We They |
| The present Present |
Am I here? Is he/she/it here? Are you/we/they here? |
I am here. He/she/it is here. You/we/they are here. |
I am not here. He/she/it is not here. You/we/they are not here. |
| Past Past |
I Was He here? She ItYou Are we here? They |
I He was here. She ItYou We were here. They |
I He was not here. She ItYou We were not here. They |
After studying the table, read the examples in Chap. "to be" in different tenses:
—My parents are rich - My parents are rich.
—It was really difficult – It was really difficult.
— Were are they happy there? – Were they happy there?
— Will you be there on time? – Will you be there on time?
The verb to be in the past tense can be studied on our website. Follow the link and begin your journey into the world of the English language.
The verb to be in English is very clear and easy. Together we learned how a verb is conjugated in the present tense, how all sentence forms are constructed, and how to answer common questions. Now that you know what the verb to be is for in English, you shouldn’t be afraid to use it in colloquial speech. Start small dialogues, and the small ones will be followed by the big ones.
After reading all the rules of the verb to be, you can do the exercises with a clear conscience. Good luck.
Verb test to be
In this test you need to show what you are capable of. Your task will be to translate several expressions that you learned today and insert the verb to be into the present simple.
Now we will get acquainted with one of the most important verbs of the English language - the verb to be, which means to be, to exist. This verb changes its form depending on in what tense and with what subject it is used. For now we will consider only the present tense.
So, in the present tense, the verb to be has three forms: am, is, are.
I am a doctor. -I am a doctor.
I am a doctor.
He is a doctor. - No is a doctor.
He is a doctor.
You are a doctor. - You are a doctor.
You are a doctor.
Using forms of the verb "to be"
So, let's take a closer look at in which case which form of the verb to be should be used:
Case 1. If we speak in the first person singular, i.e. we use the pronoun "I", which means "I", we use the form "am". Thus, it turns out “I am” - “I am.”
I am a teacher.
I'am a teacher. (I am the teacher)
Case 2.If we speak in the third person singular, using, for example, the pronouns "he, she, it", which mean "he, she, it", we use the form "is". That is, “He is” - “He is”, “She is” - “She is”, “It is” - “It is”.
She is a teacher.
Case 3. If we say “we”, which means “we”, “you”, which means “you” or “you”, and “they”, which means “they”, we must use the “are” form. For example, “We are” - “We are”, or “You are” - “You are”, “You are”, or “They are” - “They are”.
We are teachers.
We are teachers. (We are teachers)
The verb "to be" in English is often used as connection between subject and object. In all of the above examples, it performed exactly this function. Let's look at one of the proposals in more detail.
She is a teacher.
She is a teacher. (She is a teacher)
In this sentence "She" is the subject, "a teacher" - addition, and the verb "to be" is in the form "is" is a linking verb. Unlike the Russian language, in English the linking verb is never omitted, since the English sentence has a strictly fixed word order: subject + predicate + object.
Negative form of the verb "to be"
Now let's look at how the negative form of the verb "to be" is formed. It's quite simple - in order to form a negative form, you just need to put a negative particle "not" after the verb "to be":
I am happy.
I'm happy.
I am not happy.
I Not happy.
He is a doctor
He is a doctor.
He is not a doctor.
He Not doctor.
You are a teacher.
You are a teacher.
You are not a teacher
You Not teacher.
Please note that in colloquial speech the negative particle “not” often merges with the verb “to be”, forming reductions:
| is not = isn't | He is not a doctor. = He isn't a doctor. |
| are not = aren't | You are not a teacher. = You aren't a teacher. |
In English there is a very important verb “to be”, which is translated into Russian as “to be, to exist”. It is also a linking verb that connects the subject and what it is related to in a sentence.
It is also important to take into account the word order in an English sentence: subject --> predicate --> object. The predicate is necessarily present in the sentence: either it is a verb of action, or some kind of state expressed precisely by the verb to be.
For example: He is a student. / He (is) a student.
As we see, “to be” is used in English, but in the present tense it is not translated into Russian in a sentence, but is only implied.
"To be" has affirmative, negative and interrogative forms. Today we will look at the forms of this verb in the present, past and future tenses.
To be in the present tense
Verb forms: am (when we talk about ourselves), is (singular), are (plural).
- I am a teacher. - I'am a teacher.
- John is my brother. - John is my brother.
- Mary is the smartest student in the class. - Mary is the smartest student in the class.
- It is my dog's toy. - This is my dog's toy.
- We are best friends. - We are best friends.
- You are right. - You (you) are right.
- His parents are very nice. - His parents are very nice.
put the particle not
- I am not = I"m not
- He is not = He isn't
- She is not = She isn't
- It is not = It isn't
- We are not = We aren't
- You are not = You aren't
- They are not = They aren't
- Am I?
- Is he/she/it?
- Are we/you/they?
To be in the past tense
Verb forms: was (when we talk about ourselves), was (singular), were (plural).
- I was a teacher. - I was a teacher.
- John was my classmate. - John was my classmate.
- Mary was the smartest student in the class. - Mary was the smartest student in the class.
- It was his book. - It was his book.
- We were best friends. - We were best friends.
- You were right. - You (you) were (s) right.
- His parents were in London. - His parents were in London.
When we need to construct a negative sentence - put the particle not after the desired form of the verb to be. Abbreviations are also used.
- I was not = I wasn't
- He was not = He wasn't
- She was not = She wasn't
- It was not = It wasn't
- We weren't = We weren't
- You were not = You weren't
- They were not = They weren't
To ask a question, simply put the correct form of the verb to be at the beginning of the sentence. Don't forget the questioning intonation!
- Was I?
- Was he/she/it?
- We/you/they?
To be in the future tense
Verb forms: will be for all persons and numbers.
- I will be a teacher. - I'm going to be a teacher.
- John will be my colleague. - John will become my colleague.
- Mary will be the best student in the class. - Mary will be the best student in the class.
- It will be his birthday. - It will be his birthday.
- We will be best friends. - We will become best friends.
- You will be late. - You (you) will be late (be late).
- His parents will be in London. - His parents will be in London.
When we need to construct a negative sentence - put the particle not after will. Abbreviations are also used.
- I will not be = I won't be
- He will not be = He won't be
- She will not be = She won't be
- It will not be = It won't be
- We will not be = We won't be
- You will not be = You won't be
- They will not be = They won't be
To ask a question, simply put will at the beginning of the sentence. Don't forget the questioning intonation!
- Will I be?
- Will he/she/it be?
- Will we/you/they be?
Do you like the article? Support our project and share with your friends!